Difference between revisions of "Portal:Science"
KOER admin (talk | contribs) |
KOER admin (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
|{{Color-table|theme=7|title=[[Science:_Question_Papers|Question Bank]]}} | |{{Color-table|theme=7|title=[[Science:_Question_Papers|Question Bank]]}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Color-box|11|Welcome to the Science Portal|Science, as a body of knowledge as we know it today, is remarkably young, not more than a few hundred years old. And what we know also as science largely relates to the facts and explanations of everyday life. There is a need to examine what constitutes science as a process, the discipline of doing science. What are those elements of study and practice that distinguish science as an endeavour? What are the social dynamics that influence the practice of science? What are the limits of science itself? These are questions that have to be considered by a student of science. Science is also often understood as learning science as a subject and this involves the teaching and learning science and the pedagogy that must be adopted to develop a scientific bent of mind and to prepare the learner for doing science. This is a portal for students and teachers to understand and share resources on both these areas. }} | {{Color-box|11|Welcome to the Science Portal|Science, as a body of knowledge as we know it today, is remarkably young, not more than a few hundred years old. And what we know also as science largely relates to the facts and explanations of everyday life. There is a need to examine what constitutes science as a process, the discipline of doing science. What are those elements of study and practice that distinguish science as an endeavour? What are the social dynamics that influence the practice of science? What are the limits of science itself? These are questions that have to be considered by a student of science. Science is also often understood as learning science as a subject and this involves the teaching and learning science and the pedagogy that must be adopted to develop a scientific bent of mind and to prepare the learner for doing science. This is a portal for students and teachers to understand and share resources on both these areas. }} | ||
| − | <div style="float:left; width: | + | <div style="float:left; width:48%;"> |
{{Color-box|1|Interesting news| | {{Color-box|1|Interesting news| | ||
'''Did you know?''' | '''Did you know?''' | ||
| Line 89: | Line 87: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div style="width: | + | <div style="width:48%; float:right;"> |
{{Color-box|6|Topics| | {{Color-box|6|Topics| | ||
| Line 142: | Line 140: | ||
==='''Chemical reaction video magic'''=== | ==='''Chemical reaction video magic'''=== | ||
| − | {{#widget:YouTube|id=gOqdp9T-gXo|height= | + | {{#widget:YouTube|id=gOqdp9T-gXo|height=300|width=450}} |
===Which animal blood is blue in colour? === | ===Which animal blood is blue in colour? === | ||
Horseshoe crab blood is bright blue because of copper-based hemocyanin to transport oxygen where vertebrates use iron in hemoglobin. | Horseshoe crab blood is bright blue because of copper-based hemocyanin to transport oxygen where vertebrates use iron in hemoglobin. | ||
| − | {{#widget:YouTube|id=e8KlAmtIu1E|height= | + | {{#widget:YouTube|id=e8KlAmtIu1E|height=300|width=450}} |
}} | }} | ||
| + | {{Color-box|9|Spotlight| | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | === Interesting websites, videos and simulations === | ||
| + | '''STF Science videos''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{#widget:YouTube|playlist=PLWUrlh2K8RdQVclcNF-Nsh1thkSDK42QF|height=300|width=450}} | ||
| + | ===Videos by teachers from Yadgir=== | ||
| + | '''Chemical Reaction with Metals Video by Khaleelunnisa Madam from GHS Chandriki Yadgir District''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{#widget:YouTube|id=FzKF25iiT5w|height=300|width=450}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Narium Leaf Experiment Video by Jyothi Madam from GGHS Yadgir, Yadgir District''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{#widget:YouTube|id=ghWs5SQEdHc|height=300|width=450}} | ||
| + | }} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
[[Category:Science]] | [[Category:Science]] | ||
Revision as of 23:15, 4 September 2020
|
Welcome to the Science Portal Science, as a body of knowledge as we know it today, is remarkably young, not more than a few hundred years old. And what we know also as science largely relates to the facts and explanations of everyday life. There is a need to examine what constitutes science as a process, the discipline of doing science. What are those elements of study and practice that distinguish science as an endeavour? What are the social dynamics that influence the practice of science? What are the limits of science itself? These are questions that have to be considered by a student of science. Science is also often understood as learning science as a subject and this involves the teaching and learning science and the pedagogy that must be adopted to develop a scientific bent of mind and to prepare the learner for doing science. This is a portal for students and teachers to understand and share resources on both these areas. |
|
Interesting news
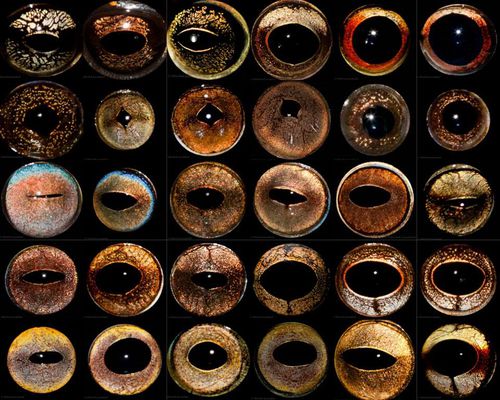
Frog Eyes!!
Tiktaalik roseae - Between fish and land animal Tiktaalik is a new species that was disovered in 2006 that has fish like features and features like a land animal. They have features of fish as well as tretrapods. Several fossils have been discovered of this fish. An extant fish Alligator Gar resembles the Tiktaalik most. Click here for more details. Why the platypus will never have a stomach Researchers have found that the animals without stomachs have completely lost the complex genes required for gastric digestion. Click here to read more. Hexagonal North Pole of Saturn There is a hexagonal cloud over the North Pole of Saturn. This was first discovered in 1980s and astronomers are trying to understand why this is happening. Click here to read more. More news HOW OUR BRAIN WORKS AND HOW SMART IS YOUR RIGHT FOOT |
|
Articles by Teachers
|
|
Famous Scientists
This highly original answer so incensed the examiner that the student was failed. The student appealed on the grounds that his answer was indisputably correct, and the university appointed an independent arbitrator to decide the case. The arbitrator judged that the answer was indeed correct, but did not display any noticeable knowledge of physics. To resolve the problem it was decided to call the student in and allow him six minutes in which to show a minimal familiarity with the basic principles of Physics. For five minutes the student sat in silence, forehead creased in thought. The arbiter reminded him that time was running out, to which the student replied that he had several extremely relevant answers, but couldn't make up his mind which to use. On being advised to hurry up the student replied as follows: "Firstly, you could take the barometer up to the roof of the skyscraper, drop it over the edge, and measure the time it takes to reach the ground. The height of the building can then be worked out from the formula . But bad luck on the barometer." "Or if the sun is shining you could measure the height of the barometer, then set it on end and measure the length of its shadow. Then you measure the length of the skyscraper's shadow, and thereafter it is a simple matter of proportional arithmetic to work out the height of the skyscraper." "But if you wanted to be highly scientific about it, you could tie a short piece of string to the barometer and swing it like a pendulum, first at ground level and then on the roof of the skyscraper. The height is worked out by the difference in the gravitational restoring force ." "Or if the skyscraper has an outside emergency staircase, it would be easier to walk up it and mark off the height of the skyscraper in barometer lengths, then add them up." "If you merely wanted to be boring and orthodox about it, of course, you could use the barometer to measure the air pressure on the roof of the skyscraper and on the ground, and convert the difference in millibars into feet give the height of the building." "But since we are constantly being exhorted to exercise independence of mind and apply scientific methods, undoubtedly the best way would be to knock on the janitor's door and say to him 'If you would like a nice new barometer, I will give you this one if you tell me the height of this skyscraper'." The student was Niels Bohr, who went on to win the Nobel Prize for Physics. For more stories about scientists click here
|
|
Book Shelf
|
|
Categories ▼ Science
|
|
Topics
|
|
From the forum
Some interesting exchanges from the STF mailing forum. Fun and magical science experiments in schoolContributed by Praveen Kamath (Kodagu), this is a compilation of simple and fun science experiments for school. Some questions and answers on biology. Read More Can scientists follow religious festivalsRead this interesting exchange on science teachers and religious observances. This was posted on the occasion of Varamahalakshmi Pooja. Speed of lightA discussion on the nature of speed of light Read More Sankranthi and Summer SolsticeThis is an interesting exchange on the dates of the Sankranthi festival and the calendar calculations. Read More . What actually is electric current?A discussion on what is electric current. Read More
|
|
Fun corner
Fun with Science Sharpen your scientific thinkingThis is an online interactive quiz available on Encyclopedia Britannica and has 60 questions on various topics of science. Play and enjoy! To access the quiz click here. Scale of the universeThis is a beautiful website that shows the dimensions of all matter in the universe - smallest to largest. To explore please click here. Chemical reaction video magic
Which animal blood is blue in colour?Horseshoe crab blood is bright blue because of copper-based hemocyanin to transport oxygen where vertebrates use iron in hemoglobin.
|
|
Spotlight
Interesting websites, videos and simulationsSTF Science videos
Videos by teachers from YadgirChemical Reaction with Metals Video by Khaleelunnisa Madam from GHS Chandriki Yadgir District
Narium Leaf Experiment Video by Jyothi Madam from GGHS Yadgir, Yadgir District
|