Difference between revisions of "Introduction to ICT the computer"
| (47 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
== '''History of computers''' == | == '''History of computers''' == | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Image:Introduction-Part3_html_m21bc9239.png|thumb | left]] | + | [[Image:Introduction-Part3_html_m21bc9239.png|thumb | left|World's First Computer]] |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Did you know, the first computer was as big as your classroom! 60 years ago,computers were very big, costly and used lot of electricity. The processors of the first computers were made using something called'vacuum tubes' - which used tubes in which electrons were moving. | Did you know, the first computer was as big as your classroom! 60 years ago,computers were very big, costly and used lot of electricity. The processors of the first computers were made using something called'vacuum tubes' - which used tubes in which electrons were moving. | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:Introduction-Part3_html_248b96c3.png|thumb|left]]<br> | + | |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Introduction-Part3_html_797aeff2.png|thumb| right|Punch Card]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Punch cards were an input method. After the vacuum tubes, came the transistors | ||
| + | which could turn electricity in a circuit 'on' or 'off'.This turning 'on' | ||
| + | and 'off' could be used to instruct computers to do calculations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Introduction-Part3_html_248b96c3.png|thumb|left|Integrated Circuit]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
During the early 1970s, with the invention of Integrated Circuits (IC) computers | During the early 1970s, with the invention of Integrated Circuits (IC) computers | ||
became faster, cheaper and smaller.Many transistors were connected together to form one IC. These computers had keyboard and monitor as input-output devices. (You will learn about input and output devices in the next chapter)... | became faster, cheaper and smaller.Many transistors were connected together to form one IC. These computers had keyboard and monitor as input-output devices. (You will learn about input and output devices in the next chapter)... | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Introduction-Part3_html_m67180220.png|right|Microprocessor]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Over the last decade, the computers became so small that it could fit in a hand. This was possible because of many integrated circuits on one | ||
| + | small square called a microprocessor or a chip which became the main part of the computer. Mouse, an input device was developed. These small and powerful computers were connected together to share information between computers and this period saw the birth and | ||
| + | growth of Internet (you will study in detail about Internet in one of the chapters). | ||
| + | Now-a-days,we see smart phones and tablets (which are small touch screen computers). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {|style="border-style: solid; border-width: 10px 20px 50px 0" | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | == '''Uses of computers''' == | ||
| + | '''Can you think of all the places where you have seen computers? | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Computers are used in many places like banks, schools, railway stations,libraries, shopping complexes, and in various fields like education,communications, business, research, development and many more. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | {|style="border-style: solid; border-width: 10px 20px 50px 0" | |
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | == '''Types of computers''' == | ||
| + | Based on the processing power, storage capacity and cost, computers are classified as, | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Introduction-Part3_html_m36a503f5.png|thumb|left|Super Computers]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(a)'''Supercomputers- The most powerful computers.They are used for highly complex problems like launching a rocket in the space or weather prediction. Supercomputers are used by universities and government agencies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Introduction-Part3_html_m7134f31.png|right|Mainframe Computers]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(b)''' Mainframe Computers - Usually slower, less powerful and cost less than supercomputers. They are used in large organisations, like banks and businesses. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Introduction-Part3_html_366ca35c.png|left|Personal Computers]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | + | '''(c)''' Microcomputers, or personal computers - The small and low cost computers. Microcomputers are more commonly known as personal computers (PC). Personal computers are further classified as (a) Stationary (b) Mobile. | |
| − | + | [[File:Introduction-Part3_html_m209f7f73.png|right|Laptop Computer]] | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(a)''' Stationary personal computers are desktop computers | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(b)''' Mobile personal computers are | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | (a) Laptop - A laptop computer popularly called laptop, or notebook computer, is a small personal computer designed for carrying where ever we go. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Introduction-Part3_html_m13a157ca.png|left|Tablet PC]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | (b) Netbook – A netbook is a small, light and low cost laptop computer. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | (c) Tablet PC - A tablet PC is a notebook or slate-shaped mobile computer. It takes input from the monitor itself, without a separate keyboard. You can input data into the computer using a stylus (digital pen), or your finger. The monitor is called touch screen. Where else have you seen touch screen monitors? | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {|style="border-style: solid; border-width: 10px 20px 50px 0" | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == '''Chapter summary''' == | |
| − | == Chapter summary == | ||
| − | |||
# Television, radio, telephone, mobile phones, computers and Internet are ICT tools. | # Television, radio, telephone, mobile phones, computers and Internet are ICT tools. | ||
# A computer is a device which takes input, processes it and gives output which can be stored and shared. | # A computer is a device which takes input, processes it and gives output which can be stored and shared. | ||
# A computer lets you do most of your daily jobs like writing a letter, solving problems, watching a film, playing games, listening to music and looking for things on the Internet. | # A computer lets you do most of your daily jobs like writing a letter, solving problems, watching a film, playing games, listening to music and looking for things on the Internet. | ||
# Latest computers are touch screen (using finger tips or stylus) computers. They are also called tablet PCs and smart phones. | # Latest computers are touch screen (using finger tips or stylus) computers. They are also called tablet PCs and smart phones. | ||
| − | + | |} | |
| − | == Exercises == | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {|style="border-style: solid; border-width: 10px 20px 50px 0" | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | == '''Exercises''' == | ||
| + | |||
'''Choose the correct answer''' | '''Choose the correct answer''' | ||
| − | + | '''(a)''' The output can be | |
| − | + | # Stored | |
| − | + | # Shared | |
| − | + | # Both (1) and (2) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''(b)''' Latest computers use | |
| − | + | # Microprocessors | |
| − | + | # Transistors | |
| − | + | # Vacuum tubes | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''(c)''' A personal computer is also a | |
| − | + | # Supercomputer | |
| − | + | # Microcomputer | |
| − | + | # Mainframe computer | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Say true or false''' | |
# ICT stands for Important Communication Technology. | # ICT stands for Important Communication Technology. | ||
# The first computer was made of vacuum tubes. | # The first computer was made of vacuum tubes. | ||
| Line 233: | Line 234: | ||
# Laptops are mainframes. | # Laptops are mainframes. | ||
# Computers can be used to learn and solve mathematics. | # Computers can be used to learn and solve mathematics. | ||
| − | + | ||
'''Activity''' | '''Activity''' | ||
| − | Some | + | Some of the uses of computers in education is given below. Think of moreuses and complete the table. |
| − | of the uses of computers in education is given below. Think of | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| border="1" | {| border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 335: | Line 333: | ||
| − | |} | + | |} |
| − | == Additional resources == | + | |
| − | + | {|style="border-style: solid; border-width: 10px 20px 20px 0" | |
| − | # Learn | + | | |
| − | # '''Learn more about computer classification''' '''[[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Classes_of_computers]]''' | + | |
| + | == '''Additional resources''' == | ||
| + | |||
| + | # '''Learn more about the history of computers''' '''[[http://www.computersciencelab.com/ComputerHistory/History.htm Computer History]]''' '''[[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_computing_hardware Computer Hardware]]''' | ||
| + | # '''Learn more about computer classification''' '''[[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Classes_of_computers Classes of Computer]]''' | ||
| + | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:36, 4 June 2014
Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) – The computer |
Introduction to ICTs and computers |
Chapter objectivesIn this chapter, you will learn about
|
Introduction to ICTs and computersYou must have heard of radio programmes like Keli kali in your school. You can see that radio, televisions, telephones, mobile phones are being used by everyone in their daily lives. Television and radio are used for giving (broadcasting) information while telephones including mobile phones are used to talk to (communicate with) your friends and family even if they are far away. Now you can carry a phone in your pocket. All these are Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) tools.
|
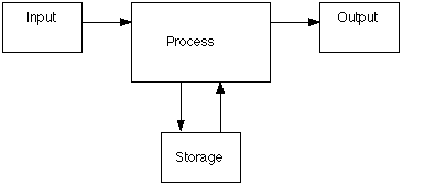
What does a computer do ?In this chapter you will learn about computers, a new ICT tool. A computer is a device which takes input, processes it and gives output which can be stored and shared. When you enter data into your computer, it is called as input. An input can be data like text or picture or an instruction (what to do with the data). This data is processed (process means to perform a series of operations on a set of data) and you will get the output. Data or information that the computer generates is called the output.
|
History of computers
Did you know, the first computer was as big as your classroom! 60 years ago,computers were very big, costly and used lot of electricity. The processors of the first computers were made using something called'vacuum tubes' - which used tubes in which electrons were moving.
|
Uses of computersCan you think of all the places where you have seen computers?
|
Types of computersBased on the processing power, storage capacity and cost, computers are classified as,
(a)Supercomputers- The most powerful computers.They are used for highly complex problems like launching a rocket in the space or weather prediction. Supercomputers are used by universities and government agencies.
(b) Mainframe Computers - Usually slower, less powerful and cost less than supercomputers. They are used in large organisations, like banks and businesses.
(a) Laptop - A laptop computer popularly called laptop, or notebook computer, is a small personal computer designed for carrying where ever we go.
|
Chapter summary
|
ExercisesChoose the correct answer
(b) Latest computers use
(c) A personal computer is also a
Say true or false
Activity
|