Difference between revisions of "Gravitation Activity 2"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (added Category:Gravitation using HotCat) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__FORCETOC__ | __FORCETOC__ | ||
| − | =Activity 2 - More about contact forces= | + | ===Activity 2 - More about contact forces=== |
| − | ===Estimated Time=== | + | ====Estimated Time==== |
30 minutes | 30 minutes | ||
| − | ===Materials/ Resources needed=== | + | ====Materials/ Resources needed==== |
Discussions | Discussions | ||
| − | ===Prerequisites/Instructions, if any=== | + | ====Prerequisites/Instructions, if any==== |
Students must have been introduced to the Newton's laws. | Students must have been introduced to the Newton's laws. | ||
| − | ===Process (How to do the activity)=== | + | ====Process (How to do the activity)==== |
#This is in the nature of discussions | #This is in the nature of discussions | ||
#Present scenarios for children to analyse | #Present scenarios for children to analyse | ||
| − | ===Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)=== | + | ====Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)==== |
#When you hang a bucket from a rope what are the forces acting? ''(Tension force is the force that is transmitted through a string, rope, cable or wire when it is pulled tight by forces from opposite ends. The tension force is directed along the length of the wire and pulls equally on the objects on the opposite ends of the wire.)'' | #When you hang a bucket from a rope what are the forces acting? ''(Tension force is the force that is transmitted through a string, rope, cable or wire when it is pulled tight by forces from opposite ends. The tension force is directed along the length of the wire and pulls equally on the objects on the opposite ends of the wire.)'' | ||
#In which direction does tension act? | #In which direction does tension act? | ||
#Is this the same as friction? When do you notice friction? ''(Frictional force is the force exerted by a surface as an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. When two objects are in contact but are not moving relative to one another then the frictional force between the two surfaces is called static friction. When the two objects are moving relative to one another, the friction between the surfaces is called the kinetic friction.)'' | #Is this the same as friction? When do you notice friction? ''(Frictional force is the force exerted by a surface as an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. When two objects are in contact but are not moving relative to one another then the frictional force between the two surfaces is called static friction. When the two objects are moving relative to one another, the friction between the surfaces is called the kinetic friction.)'' | ||
#When you push against an object, any surface, what do you feel? Do you feel a push back? Normal force is the perpendicular force that is exerted upon an object that is in contact with another stable object. If a book is resting upon a surface, then the surface is exerting an upward force upon the book in order to support the weight of the book. A normal force can also be exerted horizontally. If a person leans against a wall, the wall pushes back on the person. | #When you push against an object, any surface, what do you feel? Do you feel a push back? Normal force is the perpendicular force that is exerted upon an object that is in contact with another stable object. If a book is resting upon a surface, then the surface is exerting an upward force upon the book in order to support the weight of the book. A normal force can also be exerted horizontally. If a person leans against a wall, the wall pushes back on the person. | ||
| − | ===Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)=== | + | ====Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)==== |
[[Image:force4.png|200px|left]] Click [http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/friction here] for friction simulation | [[Image:force4.png|200px|left]] Click [http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/friction here] for friction simulation | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
#Is there any force acting in this picture between the books? | #Is there any force acting in this picture between the books? | ||
#Is gravitational force acting? | #Is gravitational force acting? | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Gravitation]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:06, 31 October 2020
Activity 2 - More about contact forces
Estimated Time
30 minutes
Materials/ Resources needed
Discussions
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Students must have been introduced to the Newton's laws.
Process (How to do the activity)
- This is in the nature of discussions
- Present scenarios for children to analyse
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- When you hang a bucket from a rope what are the forces acting? (Tension force is the force that is transmitted through a string, rope, cable or wire when it is pulled tight by forces from opposite ends. The tension force is directed along the length of the wire and pulls equally on the objects on the opposite ends of the wire.)
- In which direction does tension act?
- Is this the same as friction? When do you notice friction? (Frictional force is the force exerted by a surface as an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. When two objects are in contact but are not moving relative to one another then the frictional force between the two surfaces is called static friction. When the two objects are moving relative to one another, the friction between the surfaces is called the kinetic friction.)
- When you push against an object, any surface, what do you feel? Do you feel a push back? Normal force is the perpendicular force that is exerted upon an object that is in contact with another stable object. If a book is resting upon a surface, then the surface is exerting an upward force upon the book in order to support the weight of the book. A normal force can also be exerted horizontally. If a person leans against a wall, the wall pushes back on the person.
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
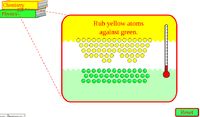
Click here for friction simulation
Answer the following questions
- What do the moving green and yellow circles indicate?
- When you are rubbing the yellow book on the green book what happens? How do you know that the heat is being generated?
- When the temperature goes very high, the yellow circles fly off. What does this mean physically?
- Is there any force acting in this picture between the books?
- Is gravitational force acting?