Difference between revisions of "Central tendency"
KOER admin (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "<mm>[[" to "[[File:") |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
= Concept Map = | = Concept Map = | ||
__FORCETOC__ | __FORCETOC__ | ||
| − | + | [[File:central_tendency_eng.mm|Flash]]</mm> | |
= Textbook = | = Textbook = | ||
Revision as of 18:59, 17 May 2017
| Philosophy of Mathematics |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist.
Concept Map
</mm>
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional Information
Useful websites
- This pdf short notes gives simple definitions of mean, median, mode click here [1]
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arithmetic_mean
- https://explorable.com/arithmetic-mean
- http://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Arithmetic_mean.html
Reference Books
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1.MEAN
The mean (or average) is the most popular and well known measure of central tendency. It can be used with both discreteand continuous data, although its use is most often with continuous data. The mean is equal to the sum of all the values in the data set divided by the number of values in the data set. So, if we have n values in a data set and they have values x1, x2, ..., xn, then the sample mean, usually denoted by
![]() (pronounced x bar), is:
(pronounced x bar), is:
The mean includes every value in your data set as part of the calculation. In addition, the mean is the only measure of central tendency where the sum of the deviations of each value from the mean is always zero.
Learning objectives
- Understand and know that a measure of central tendency is a single value that attempts to describe a set of data by identifying the central position within that set of data.
- Understand that the mean, median and mode are all valid measures of central tendency but, under different conditions, some measures of central tendency become more appropriate to use than others.
- Learn to calculate mean and analyse data and make inferences.
Notes for teachers
A measure of central tendency is a single value that attempts to describe a set of data by identifying the central
position within that set of data. As such, measures of central tendency are sometimes called measures of central location. They are also classed as summary statistics. The mean (often called the average) is most likely the measure of central tendency that you are most familiar with, but there are others, such as, the median and the mode.
The mean, median and mode are all valid measures of central tendency but, under different conditions, some measures of
central tendency become more appropriate to use than others.
Activity
- Activity No #1 central tendency mean activity1
- Activity No #2 central tendency mean activity2
Concept #2.MEDIAN
Learning objectives
- Understand the median as a measure for central tendency
- Understand when and when not to use median
Notes for teachers
The median is the middle score for a set of data that has been arranged in order of magnitude. The median is less affected by outliers and skewed data.
Activity
- Activity No #1 central tendency median activity1
- Activity No #2 central tendency median activity2
Concept #3.MODE
Learning objectives
- Understand the mode as a measure for central tendency
- Understand when and when not to use mode
Notes for teachers
The mode is the most frequent score in our data
set. On a histogram it represents the highest bar in a bar chart or
histogram. You can, therefore, sometimes consider the mode as being
the most popular option. An example of a mode is presented below:
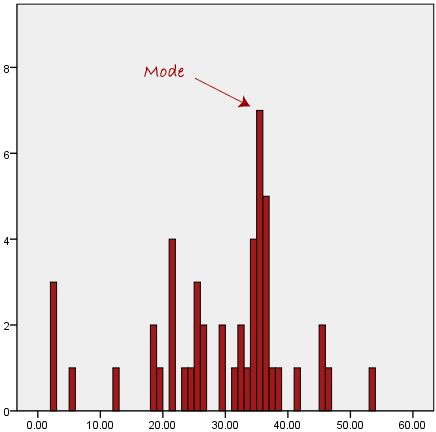
Normally, the mode is used for categorical data where we wish to know which is the most common category
Activity
- Activity No #1 central tendency mode activity1
- Activity No #2 central tendency mode activity2
Hints for difficult problems
Project Ideas
Math Fun
Usage
Create a new page and type {{subst:Math-Content}} to use this template