Difference between revisions of "Nature of Light"
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
* '''Question Corner''' | * '''Question Corner''' | ||
| − | ===Activity No # 1B - Corpsucular Theory of Light === | + | ===Activity No # 1B - What is colour === |
| + | {| style="height:10px; float:right; align:center;" | ||
| + | |<div style="width:150px;border:none; border-radius:10px;box-shadow: 5px 5px 5px #888888; background:#f5f5f5; vertical-align:top; text-align:center; padding:5px;"> | ||
| + | The objective is to understand colours as different wavelengths associated with light. | ||
| + | * '''Estimated Time''' - 30 minutes | ||
| + | * '''Materials/ Resources needed''' | ||
| + | Computer, projector, power | ||
| + | * '''Prerequisites/Instructions, if any''' | ||
| + | * '''Multimedia resources''' | ||
| + | {{#widget:YouTube|id=UZ5UGnU7oOI}} | ||
| + | * '''Website interactives/ links/ simulations''' | ||
| + | * '''Process (How to do the activity)''' | ||
| + | Watch the video and discuss with the student their understanding. | ||
| + | * '''Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)''' | ||
| + | #How does a wave move? The vocabulary is wave propagation) | ||
| + | #What gets transmitted? | ||
| + | #What can you say about the wave when the frequency is high? | ||
| + | #What can you say about the wave when the wavelength is high? | ||
| + | #It is possible to look at light as a wave; the waves are not of material objects but travelling waves changing electric and magnetic fields. | ||
| + | #Different wavelengths are associated with different energy levels and different kind of radiation(light is a form of electromagnetic radiation; there are other electromagnetic radiations) | ||
| + | #The higher the frequency the higher the energy; this is seen as different colours of the visible spectrum | ||
| + | #Can we break down these seven colours more? (No; demonstrate with a prism; these are pure colours) | ||
| + | * '''Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)''' | ||
| + | Draw a ray diagram to show how this theory explains reflection. | ||
| + | * '''Question Corner''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Activity No # 1C - Corpsucular Theory of Light === | ||
{| style="height:10px; float:right; align:center;" | {| style="height:10px; float:right; align:center;" | ||
|<div style="width:150px;border:none; border-radius:10px;box-shadow: 5px 5px 5px #888888; background:#f5f5f5; vertical-align:top; text-align:center; padding:5px;"> | |<div style="width:150px;border:none; border-radius:10px;box-shadow: 5px 5px 5px #888888; background:#f5f5f5; vertical-align:top; text-align:center; padding:5px;"> | ||
| Line 117: | Line 143: | ||
Draw a ray diagram to show how this theory explains reflection. | Draw a ray diagram to show how this theory explains reflection. | ||
* '''Question Corner''' | * '''Question Corner''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Concept #2 - Wave Nature of Light== | ==Concept #2 - Wave Nature of Light== | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 20 January 2014
| Philosophy of Science |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist
Concept Map
Error: Mind Map file Nature_of_Light.mm not found
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional information
Useful websites
- Interactive Simulation on Nature of Light

In this simulation, you can explore the history of quantum physics, how the understanding of light was developed and an overview of the theories of light. Source: NSTA - Interactive Simulation on Nature of Light

In this simulation you can explore the behaviour of light as waves. Source: NSTA - Wikipedia article on Wave Particle Duality
- Web interactives and additional information on Physics of Light and Colour; Source: Olympus Microscopy Research
- Physics Classroom-Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Classroom-Wavelike Properties of Light
- Physics Classroom - Electromagnetic Radiation and Visible Spectra
Reference Books
- E=m by David Bodanis - This book is a very interesting account of how the understanding developed in quantum physics and the theory of light. See Online
- NCERT Textbook Chapter Light
- NCERT Textbook Chapter Reflection and Refraction
- NCERT Textbook Chapter Human Eye and the Colourful World
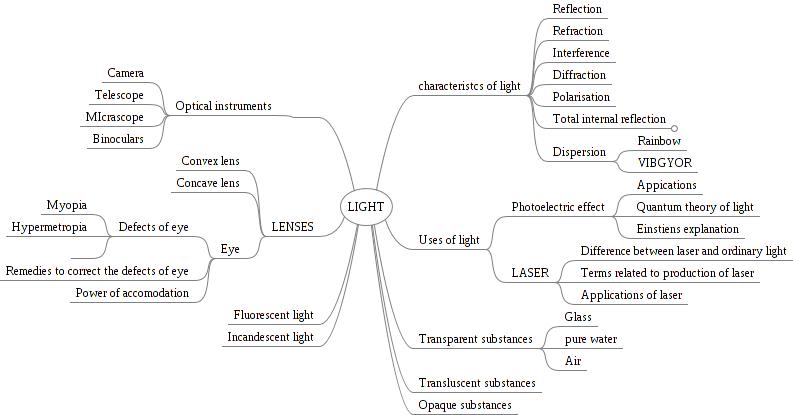
An image of a concept map of light
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1 - White Light is made up of colours
Learning objectives
- White Light is made up of seven constituent colours
- Introduction to the corpuscular theory of light
Notes for teachers
Reinforce the learning from activity on Recombination of Colours. Also understand the model as proposed by Newton on the nature of light and examine the limitations of this theory.
| LCs8mK1rzc0|150|left}} Primary Additive Colours |
r8ejTUNwgTo|150|left}} Primary Subtractive Colours |
Activity No # 1A - Using a prism to split and combine white light
- Estimated Time - 2 periods of 40 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed
White paper, Pins, Source of Light, Prisms, Dark room
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Activity on Recombination of Colours
- Dark room for light experiments
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ simulations
| Newton's Prism Experiment. This is a demonstration of the experiment showing the splitting and recombination of white light. Useful to show the students after the demonstration/ experimentation in class. |
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Demonstrate the dispersion using a prism and recombination of the light
- Students must do this experiment in groups
- The teacher must demonstrate carefully how to position the prism, how to observe rays in light experiments
- Students must be able to draw ray diagrams showing the split of the spectrum
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- When the light falls on the prism, what did you expect to see? What happened?
- What are the colours you see? What is the order of the colours?
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- From the incoming beam of light, which colour showed the maximum angle of dispersion? (This question can be picked up later to discuss wavelengths and electromagnetic spectrum)
- If you change the direction of the incoming light, what happens to the dispersion?
- Observe the accuracy of the diagrams
- Question Corner
Activity No # 1B - What is colour
The objective is to understand colours as different wavelengths associated with light.
Computer, projector, power
Watch the video and discuss with the student their understanding.
Draw a ray diagram to show how this theory explains reflection.
Activity No # 1C - Corpsucular Theory of LightThe objective is to study Newton's theory on light
Computer, projector, power
Watch the video and discuss with the student their understanding.
Draw a ray diagram to show how this theory explains reflection.
Concept #2 - Wave Nature of LightLearning objectives
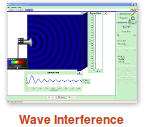
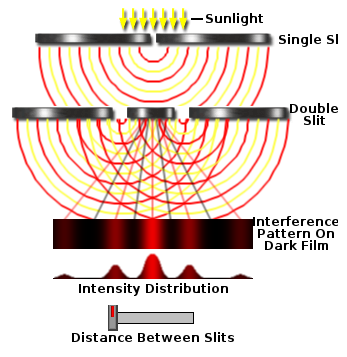
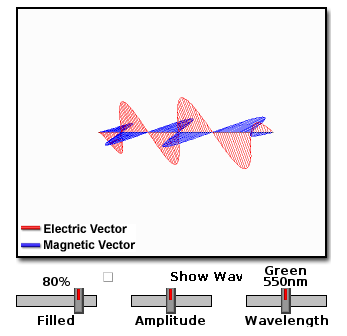
Notes for teachersStudies done on how light travels has helped us visualise it now as changing electrical magnetic fields that interact with other material objects as packets of energy. This radiation can be thought of as waves of different wavelengths. The waves are not of material objects but travelling waves changing electric and magnetic fields. Different wavelengths are associated with different energy levels and different kind of radiation. Click here for more notes on the nature of light, visible light and colours. Videos on Nature of Light Activity No # 1 - Simulation of double slit experimentThe objective of this activity is to demonstrate an important experiment from the 18th century that made physicists rethink about the nature of light.
Activity No # 2- Explain the double slit experiment
Computer, Projector, Blackboard
Simulation of the double slit experiment
After discussing the simulation, explain the process of interference in waves
Observe the student response to above questions
Concept # 3- Dual Nature of LightLearning objectives
Notes for teachersThe objective here is to enable students to understand that light can be thought of as a wave or as particles. Different models of light explain different phenomena. It is important to get a sense of the history of how light was understood, how electromagnetism was understood and how light is the result of continuously oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Activity No #1 - Introduce the nature of electromagnetic radiation
Activity No #
Concept #4 Electromagnetic Spectrumhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lwfJPc-rSXw&list=PL09E558656CA5DF76 Learning objectivesNotes for teachersThese are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes. Activity No #
Activity No #
Project IdeasFun cornerUsage Create a new page and type {{subst:Content}} to use this template
|