Triangles
Revision as of 07:12, 14 August 2015 by suchethass (talk | contribs) (→Activity No # 2. property of a triangle)
| Philosophy of Mathematics |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist.
Concept Map
Error: Mind Map file Triangles .mm not found
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional Information
http://www.mathopenref.com/similartriangles.html
Useful websites
- All about triangles :This is a reference website for types and classification off triangles
- http://www.regentsprep.org/regents/math/geometry/GPB/theorems.htm :A good website for quick reference of all theorems in geometry. Suitable for both students and teachers.
- Click here for notes on types of triangles.
Reference Books
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1 A triangle and its basic properties
Learning objectives
- A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments.
- It is the polygon with the least number of sides.
- A triangle can be defined as a polygon which has 3 sides, 3 angles and 3 vertices.
- The sum of any two sides is always greater than the third side.
- The angle opposite to longest side is the largest.
- The angles inside the triangle are its interior angles.
- The sum of all 3 interior angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees which is called the angle sum property of a triangle.
- The external angle of a triangle is always equal to the sum of its two opposite interior angles.
Notes for teachers
[These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.]
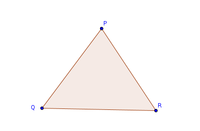
- A triangle PQR consists of all the points on the line segment PQ,QR and RP. The three line segments, PQ, QR and RP that form the triangle PQ, are called the sides of the triangle PQR.
- A triangle has three angles. In figure, the three angles are ∠PQR ∠QRP and ∠RPQ
- A triangle has six parts, namely, three sides,PQ QRand RP.Three angles ∠PQR ∠QRP and ∠RPQ. These are also known as the elements of a triangle.
- The point of intersection of the sides of a triangle is known as its vertex. In figure, the three vertices are P, Q and R. In a triangle, an angle is formed at the vertex. Since it has three vertices, so three angles are formed. The word triangle =tri + angle ‘tri’ means three. So, triangle means closed figure of straight lines having three angles.
Activity No # 1 Make your triangle
- Estimated Time - 40 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed; Paper, pencil, and scale.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any:
- The students should know points and line segments.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ Geogebra Applets
- Process (How to do the activity):
- Mark three non-collinear point P, Q and R on a paper.
- Join these points in all possible ways. The segments are PQ, QR and RP.
- A simple close curve formed by these three segments is called a triangle. It is named in one of the following ways.
- Triangle PQR or Triangle PRQ or Triangle QRP or Triangle RPQ or Triangle RQP .
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions):
- What are plane figures ?
- What is a polygon ?
- How many points are needed to make a traingle ?
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child):
- What are the intersecting points of a triangle called ?
- Can you draw a triangle with collinear points.
- Question Corner
- Name the elements of a triangle.
Activity No # 2. Angle sum property of a triangle
Please click the following link for the proof
- Estimated Time: 40 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed:Laptop, projector, geogebra file and a pointer.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any:
- Basics of triangles should have been covered.
- Angles formed when a traversal cuts a pair of parallel lines and the relationship between them should have been taught.