Similarity and Congruence
| Philosophy of Mathematics |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist.
Concept Map
Error: Mind Map file 5a._Similar_and_Congruent_triangles.mm not found
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional Information
Useful websites
Reference Books
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1 - Understanding similarity
Learning objectives
- To show similar planar figures, discuss congruence and properties of congruent/ similar triangles
Notes for teachers
These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.
Activity No #1 Identifying similar shapes, similar triangles
- Estimated Time - 80 minutes (40 +40)
- Materials/ Resources needed - Blackboard, Geogebra files + projector, Calculator
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ Geogebra Applets
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Draw figures on the boards - planar figures and triangles
- Draw pairs of figures on the board [ both similar and dissimilar]; they can identify overlap of congruent figures
- Demonstrate using Geogebra files and discuss
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Can you identify similar figures?
- If the children know the names of the theorem, can they explain SSS, AAA, ASA?
- What does a ratio of side mean? What is proportionality?
- In the Geogebra files, when I change the sides/ proportion, the triangles change in size. But the proportion remains the same, angle remains the same
- With calculator verify the proportion (this is very very useful for involving the whole class) they all can see the proportion remains constant though the size changes
- Show the arithmetic behind the proportion
- Note - When there is a wrong answer, identify what is the source of the confusion – sides, ratio and proportion
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Distinguish congruence and similarity
- Can they relate the theorem to the facts and figures?
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ Geogebra Applets
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Concept #
Learning objectives
Notes for teachers
These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ Geogebra Applets
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
Suchetha . S. S Asst. Teacher ( Mathematics ) GJC Thyamagondlu. Nelamangala Talluk Bangalore Rural District doing the activity below on a lesson on similar triangles using GeoGebra in the classroom
- Website interactives/ links/ Geogebra Applets
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Hints for difficult problems
Project Ideas
Math Fun
Usage
Create a new page and type {{subst:Math-Content}} to use this template
Pythagorean Theorem
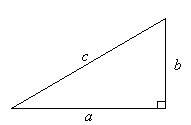
Pythagoras' Theorem was discovered by Pythagoras, a Greek mathematician and philosopher who lived between approximately 569 BC and 500 BC.
Pythagoras'
Theorem states that:
In
any right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal
to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. That is:
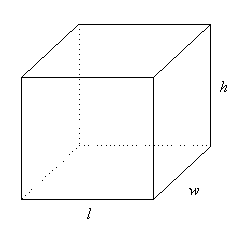
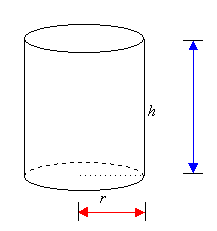
Pythagoras' Theorem in
Three Dimensions
A
three-dimensional object can be described by three measurements -
length, width and height.
We
can use Pythagoras' Theorem to find the length of the longest
straw that will fit inside
the
box or cylinder.
GeoGebra Contributions
- The GeoGebra file below to understand Similar Triangles
- Similar Triangles Part 1 http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/Maths/Similar_Triangles_1.html
- Download ggb file here http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/Maths/Similar_Triangles_1.ggb
- Similar Triangles Part 2 http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/Maths/Similar_Triangles_2.html
- Download ggb file here http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/Maths/Similar_Triangles_2.ggb
- Similar Triangles Part 3 http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/Maths/Similar_Triangles_3.html
- Download ggb file here http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/Maths/Similar_Triangles_3.ggb
- See a video to understand this concept http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BI-rtfZVXy0
- The GeoGebra file below verifies the Thales theorem
- Thales Theorem http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/Maths/thales_theorem.html
- Download ggb file here http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/Maths/thales_theorem.ggb
- See a video that proves this theorem http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y-6yYsuGLoc