Light
| Philosophy of Science |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist
Concept Map
Error: Mind Map file Light.mm not found
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional information
Useful websites
Reference Books
An image of a concept map of light
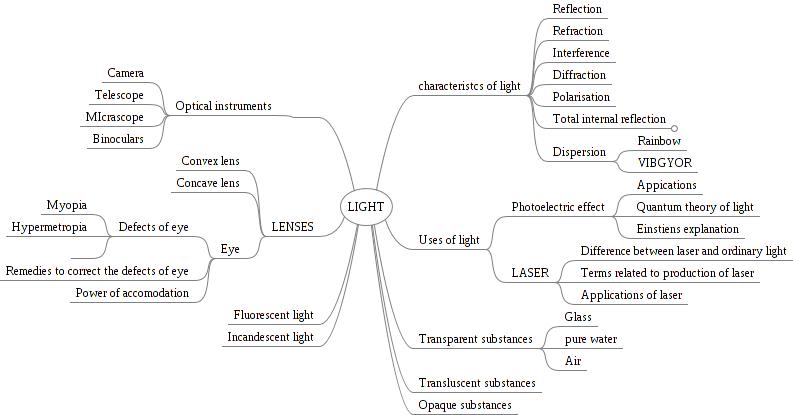
Teaching Outlines
- Light is a form of energy
- Light travels as electromagnetic radiation; with waves of different wavelengths
- Light interacts with material particles in discrete packets called photons
- Different wavelengths are associated with photons of different energies
Concept #1 - Light is a form of energy
Learning objectives
- Light is a form of energy and travels as electro-magnetic radiation. There are other radiations apart from light that travel as electro-magnetic radiation.
- It is possible to look at light and other electro magnetic radiation as a wave or as a particle known as the photon.
Notes for teachers
These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.
- Light is a form of energy that is transported as electromagnetic radiation but interacts with material particles as discrete packets of energy that are called photons.
- Sun provides us with heat and light. This travels through the near vacuum of space. So there is no material to transport energy. #When we block light we also block the heat radiation. Any source of heat also radiates some visible light.
- This radiation can be thought of as waves of different wavelengths. The waves are not of material objects but travelling waves changing electric and magnetic fields. Different wavelengths are associated with different energy levels and different kind of radiation.
| The following video is useful to see the development of theories of light. |
Listen to Richard Feynman, renowned physicist talk about the nature of light. |
| J1yIApZtLos| 150| left}} | ceTT3mFVaIM| 150| left}} |
Activity No # 1 - Thought Experiment - Radiation from the Sun
- Estimated Time - 30 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed - None
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any - None
- Multimedia resources
This is a video that explains radiation as an animation. Use this to initiate the discussion and talk about the questions below.
- Website interactives/ links/ simulations
- Process (How to do the activity)
Heat a piece of iron and the iron changes colour from a dull grey to red to yellow to white when light of all wavelengths are radiated in addition to the heat. On a cold day the temperature inside a glass house is much higher – why? Because light of a shorter wavelength can travel through glass and is absorbed by the ground and plants. The ground reflects back radiation of a higher wavelength – infra-red and heat radiation. This cannot pass through glass and so the glass house is much warmer.
Keep a black cloth under light and it will be distinctly warmer after sometime.
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
From all this can we see the following:
- What happens to the energy from the sun? - Energy is transported from a source to a destination without a medium
- Are there different kinds of energy/ forms of energy? - The energy is of different kinds – heat, light of different colours, X ray, eyc.
- What happened here when you places something in the sun? - One form of the energy can get converted to another. They must therefore have things in common - radiant heat and light are similar in many ways and different in some ways.
Explain
Studies done on how light travels has helped us visualise it now as changing electrical magnetic fields that interact with other material objects as packets of energy.
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ simulations
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Concept #
Learning objectives
Notes for teachers
These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ simulations
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ simulations
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Project Ideas
Fun corner
Usage
Create a new page and type {{subst:Science-Content}} to use this template