Difference between revisions of "Plantae"
| Line 180: | Line 180: | ||
40 minutes | 40 minutes | ||
| − | ==Materials/ Resources needed== | + | ==Materials/ Resources needed== |
| + | #Microscope | ||
| + | #glass slides and cover slips | ||
| + | #stain | ||
| + | #stem of a pteridophyte | ||
| + | #cutter,watch glass and water | ||
| + | |||
==Prerequisites/Instructions, if any== | ==Prerequisites/Instructions, if any== | ||
==Multimedia resources== | ==Multimedia resources== | ||
Revision as of 16:50, 20 February 2015
| Philosophy of Science |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist
Concept Map
__FORCETOC_
Error: Mind Map file Kingdom Plantae.mm not found
Teaching Outlines
Multicellular algae
Learning objectives
- students explains the body structure of multicellular algae
- students explains the important characteristics of multicellular algae
- students differentiates multicellular algae based on pigmentation
- students observe specimens of multicellular algae in a micro scope
- students draw the diagrams of multicellular algae
Notes for teachers
- Multicellular algae have undifferentiated thalloid body structure
- Based on pigmentation they are classified into three groups,they are Green algae,Brown algae and Red algae
- Gametophytic plant body is predominant
- They exhibit vegetative,asexual and sexual reproduction
- They are primitive thallophytic plants
Activity No 1 - Collecting specimens of algae
Estimated Time
Based on the source of collection(distance from the school)
Materials/ Resources needed
- formalin solution
- glass/transparent plastic jars
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Select shallow water bodies
Superwise students while collecting specimens from water bodies
Multimedia resources
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- How is the structure of algae that you have collected?
- How algae are different from higher plants?
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Explain the pigmentation in algae?
- Explain the thalloid structure of algae?
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
Bryophytes
Learning objectives
- students explains the body structure of bryophytes
- students realizes the importance of rhizoids in bryophytes
- students describes the life cycle of bryophytes
- students understands the dominance of gametophyte in the life cycle of bryophytes
- students explains the reproduction in bryophytes
- students admires the economic importance of brtophytes
Notes for teachers
- Bryophytes are considered as amphibians of plant kingdom,usualy habituate damp soil
- Rhizoids,a root like structure helps to absorb water and minerals from soil
- There are two phases in life cycle,gametophyte is dominant,whereas sporophyte is small and dependent on gametophyte
- They are non vascular plants
- They exhibit both sexual and asexual reproduction
- In the gametophyte,antheridium(male reproductive structure)and archaegonium(female reproductive structure)are present
Activity1
Activity No 1 - 'Observation of gametophyte and sporophyte in Bryophytes'
Estimated Time
40 minutes
Materials/ Resources needed
Sporophytic and gametophytic generation of any Bryophyte
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Students are instructed to go through the text book content on bryophytes
Multimedia resources
File:I10-22a-bryophytes.jpg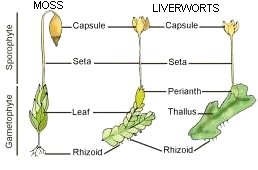 File:life-cycle-funaria-small.GIF
File:life-cycle-funaria-small.GIF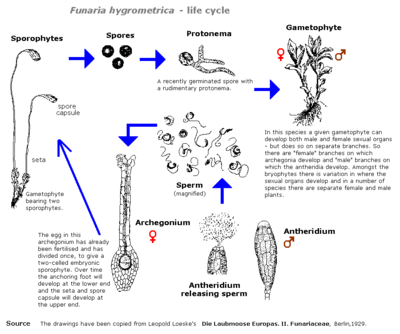
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Instruct students to observe the gametophyte and sporophyte of bryophyte ask them to draw their observation
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Is the sporophyte independent of gametophyte?
- What is the major difference that you observe between gametophyte and sporophyte?
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- What are the two phases of life cycle in bryophytes?
- What are the differences between gametophyte and sporophyte in bryophytes?
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
Pteridophytes
Learning objectives
- students realizes the evolution of vascular tissues in pteridophytes
- students explains the important characteristics of pteridophytes
- students describes the life cycle in pteridophytes
- students understands the dominance of sporophytic plant body in pteridophytes
- students explains reproduction in pteridophytes
- students appreciates the ecomic and aesthetic importance of pteridophytes
Notes for teachers
- Pteridophytes are the first evolved vascular plants
- Plant body is differentiated into root,stem and leaves
- There are two phases in life cycle,sporophyte is dominant,whereas gametophyte is small,but independent
- Their gametophyte is called as prothallus
- They usually found in humid shadow habitats
- They exhibit both sexual and asexual reproduction
Activiti
=Activity No 1 - 'Observation of sporophyte and gametophyte in Pteridophytes'
Estimated Time
40 minutes
Materials/ Resources needed
Specimens of sporophyte and gametophyte of given Pteridophyte
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Instruct students to refer text book content on Pteridophytes before the activity
Multimedia resources
File:ferns.gif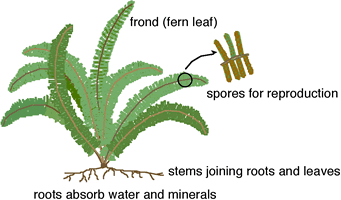 File:Life cycle of a Heterosporous Pteridophyte.jpg
File:Life cycle of a Heterosporous Pteridophyte.jpg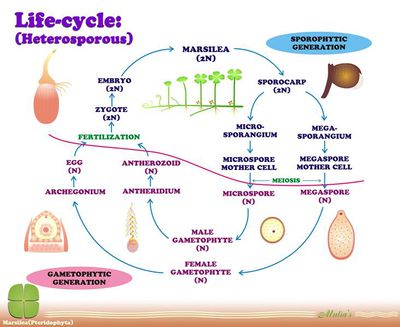
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- What is the major difference that you observed between gametophyte and sporophyte in pteridophytes?
- Is gametophyte independent from sporophyte in pteridophytes?
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Explain the life cycle in Pteridophytes?
- Write the differences between sporophyte and gametophyte in Pteridophytes?
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
Activity No 2 - mioroscopic observation of vascular bundles in pteridophytes
Estimated Time
40 minutes
Materials/ Resources needed
- Microscope
- glass slides and cover slips
- stain
- stem of a pteridophyte
- cutter,watch glass and water
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Multimedia resources
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
Activity No # 1 - Name of Activity
Estimated Time
Materials/ Resources needed
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Multimedia resources
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
- Collect the specimens of Pteridophytes in your locality and observe their body structure
- Take a transverse section of stem of any pteridophytic plant you have collected and observe vascular bundles(steles)
Gymnosperms
Learning objectives
- students explains the important characteristics of gymnosperms
- students realizes the significance of bare seeds in gymnosperms
- students explains the structure and function of cones in gymnosperms
- students explains the reproduction in gymnosperms
- students understands the evolutionary significance of diminishing gametophyte
Notes for teachers
- Gymnosperms have distinguished naked seeds without seed cover in their plantbody
- They are characterized by cones,male cone is a bundle of microsporophylls,whereas female cone is a bundle of megasporophylls
- They are perenial trees or shrubs,found in xerophytic, temperate and polar habitat
- Vascular tissues are more advanced than pteridophytes
- Cones are the gametophytic structures,rest of the plantbody is sporophyte
- cones(gametophyte)are entirely dependent and a part of dominant sporophytic plant body
Activities
Activity No 1 - collecting male and female cones of gymnosperms
Estimated Time
Materials/ Resources needed
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Multimedia resources
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
Activity No 2 - observing seeds of cycas/thuja
Estimated Time
Materials/ Resources needed
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Multimedia resources
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
Activity No # 1 - Name of Activity
Estimated Time
Materials/ Resources needed
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Multimedia resources
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
- Collect male and female cones of Thuja or Cycas in your locality and compare the differences between male and female cones
- Observe mega spores and micro spores under microscope
Angiosperms
Learning objectives
- students explains the important characteristics of angiosperms
- students realizes the significance of fruit covered seeds in angiosperms
- students explains the structure and function of flowers in angiosperms
- students explains the reproduction in gymnosperms
- students understands the evolutionary significance of diminishing gametophyte
- Students differentiates monocots from dicots
Notes for teachers
- Angiosperm are most advanced and highly evolved class among plants
- They are characterized by seed covered by fruit
- They are all flower bearing plants,specialized shoot bearing bunch of flowers is called as inflorescence
- There are two groups,monocots and dicots based on number of cotyledons in the seed
- The entire plantbody is sporophyte except androecium and gynoecium(they are the only gametophytic representatives in entire plant)
- The vascular bundles are highly evolved than gymnosperms and pteridophytes
- They exhibit rich diversity when compared to other classes of plants
Activities
Activity No # 1 - observing venation in leaves of dicot and monocot plants
Estimated Time
Materials/ Resources needed
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Multimedia resources
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
Activity No # 2 - observing germination of dicot and monocot seeds
Estimated Time
Materials/ Resources needed
Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Multimedia resources
Website interactives/ links/ simulations
Process (How to do the activity)
Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
Question Corner
To link back to the topic page Give the link of the page name from where activity was given Back
Assessment Activities for CCE
- Write an essay on 'evolutionary trend in different classes of Kingdom Plantae'
- Prepare herbarium of monocot and dicot leaves to compare venation
- Germinate monocot and dicot seeds,observe the growth and record your observation
- Collect the representative specimens of all the classes of Plantae and record the differences in their body structure.
Project Ideas
- Conduct a micro survey of monocot and dicot plants in your locality
- Project on,'comparative study of evolution of vascular bundles in plants'

