Organisms
| Philosophy of Science |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist
Concept Map
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional information
Useful websites
Reference Books
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1 - What defines an organism
Learning Objectives
- To develop an understanding of what is an organism
- To appreciate diversity
Notes for teachers
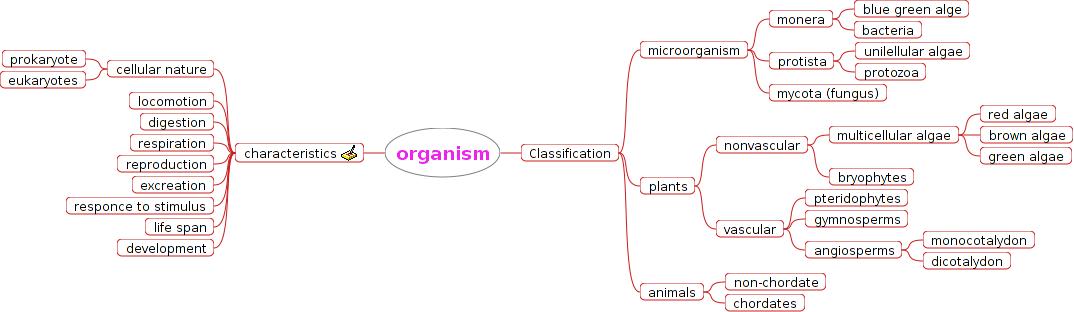
Classification of organisms

In
this section we will explore the following key concepts:
- What are the characteristics of organisms?
- How can we study organisms?
- What are the similarities and dissimilarities?
- What are the methods of studying organisms?
Learning objectives
Notes for teachers
These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ simulations
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ simulations
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Concept #
Learning objectives
Notes for teachers
These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ simulations
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ simulations
- Process (How to do the activity)
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions)
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child)
- Question Corner
Project Ideas
Fun corner
Usage
Create a new page and type {{subst:Science-Content}} to use this template
Concept Map
Concept #1 - Diversity in organisms and their classification
Learning Objectives
- To appreciate diversity
- To classify organisms
Notes for teachers
Every organism whether plant or animal is unique in itself. There is a wide diversity in the flora (plants) and fauna (animals) in the world. The diversity we see today is the result of 3.5 billion years of organic evolution. During the course of this evolution several species vanished from the surface of the Earth and became extinct. It is estimated that more than fifty times the existing species have become extinct. With such a vast number of organisms - both living and extinct, it becomes impossible to study every one of them at individual level. This task of studying the diversity of living organisms can be made easier and more effective if the various organisms are arranged in an orderly manner.
Classification is one such method of studying living organisms in a systematic
manner. By making a comparative study and assorting the similarities and differences amongst the various
varieties of species, organisms can be classified into groups or
sets. Systematics is the study of the diversity of organisms with
their environments.
Activity #1 - Diversity in organisms
Objectives
- Understand about the variety of animal and plant life through direct observation, activities and by using secondary sources like videos, pictures,etc.
- To develop skills of recording and classification
Method
- Nature of Activity: pair work
- Materials required: Pen and work sheet (Note book)
- Time Required: 30 Minutes.
- Video-clippings
Procedure (part 1):
Teacher tells students to compare their nose , hair, and eye with their friend's and find differences in size and colour. To compare horse with donkey, monkey and gorrilla. What similarities are found between these animals? Which two animals can be grouped as having common characteristics? What is the basis of our identification? In this activity, we had to decide which characteristics were more important in forming the desired category. Now, think of all the different forms in which life occurs on earth. Watch the video-clippings and the various kinds of animals that live there.
Procedure (part 2):
Time required : 30 minutes
Give instruction to students to watch the video/ pictures
carefully and to make notes on what they observed and listened.
Students must now make a list of
animals and plants which have similar structure,
shape and size. And their differences. Encourage
students to identify unfamiliar plants/ animals or new words while
watching video-clippings/ photos/ pictures etc. and raise their hands
to ask for meaning, definition etc.
Discussion questions
- What do we mean by an ecosystem? What are the characteristics you saw in the ecosystem? What processes were seen there?
- Will similar processes and characteristics of organisms be found in other systems?
- Are living organisms machines?
- Why do you think there are so many differences? What might have been the processes that caused this diversity
Additional web resources
www.edu.gov.nf.ca/division/stsuppsv/Junhigh/grad9sci.pdf
This
is a reference document for planning a unit on diversity of
organisms.
Methods of classification
Classification
is a grouping
of organisms, (plants or animals) in different ranks on the basis of
their characters. Systematics is the study of organisms based on the
interactions with the environment. Systematics(systema
- order) - The camparative study of organisms on the basis of
morphology, anatomy, ecology, physiology, biochemistry etc. is known
as systematics.
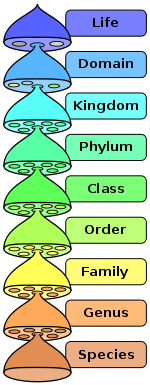
Systematics
have three fields (i) Nomenclature (ii) Classification (iii)
Taxonomy. Taxonomy
(Taxis
- arrangement, nomous = law / rule) is the branch of biology for the
study of classification of organisms following certain rules or
principals.
What is the Basis of Classification?
Attempts at classifying living things into groups have been made since time immemorial. Greek thinker Aristotle classified animals according to whether they lived on land, in water or in the air. This is a very simple way of looking at life, but misleading too. For example, animals that live in the sea include corals, whales, octopuses, starfish and sharks. We can immediately see that these are very different from each other in numerous ways. In fact, their habitat is the only point they share in common. This is not an appropriate way of making groups of organisms to study and think about. We therefore need to decide which characteristics to be used as the basis for making the broadest divisions. Then we will have to pick the next set of characteristics for making sub-groups within these divisions. This process of classification within each group can then continue using new characteristics each time.
Taxonomy is a regular branch of science that
is involved with the purpose of arranging or grouping organisms.
Importance of classification
- It makes the study of such a wide variety of organisms easy.
- It projects before us a good picture of all life forms at a glance.
- It helps us understand the interrelationship among different groups of organisms.
- It serves as a base for the development of other biological fields such as biogeography .
- Various fields of applied biology such as agriculture, public health and environmental biology depend on classification of pests, disease vectors, pathogens and components of an ecosystem.
History of Classification:
Classification of living organisms is probably as old as human civilization. Organisms have been grouped on different basis at different periods of time. The earliest classification was probably on the basis of utility to man. Plants and animals were classified on different basis such as edible and non-edible ones, useful and harmful ones and so on.
History of systematics
Father of taxonomy -Carolus Linnaeus
(Books
- Species plantarum & systema naturae) and Philosophica
Botanique
Taxonomy term - de
Candolle
Systematics
term - C.
Linnaeus
Father
of Botany - Theophrastus.
(He
had written the book Historia plantarum and Enquiry into the
plants)
Father of Indian Taxonomy -Santapau
New
Systematics - Or Biosystematics - Classification of organisms on the
basis of evolution, genetical & morphological traits. It is the
another field of systematics.
New
systematics-term by - Julian Huxley
Biosystematics-term by -Camp
& Gilly '[[4]]
Types of Taxonomy
(i)
Chemotaxonomy - (Biochemical Systematics) - Classification based on
chemicals present in organisms
(ii) Numerical Taxonomy - (or
phenetics or Adansonian classification) - Classification based on
number of shared characters of various organisms.
(iii)
Cytotaxonomy (Alston & Turner) - Classification based on nuclear
& chromosomal studies
Activity : Introduction to classification
Objectives
To introduce the method of classification
To observe, record and classify organisms in an environment
Method
- Nature of Activity: Group /Individual.
- Materials required: Pen and work sheet (Note book).
- Books and periodicals in a library
Procedure (part 1)
- Teacher can develop the concept of importance of classification by illustration through comparing arrangement of books and periodicals in a library.
- Have the students organize books (reference-text), periodicals (weekly, monthly and yearly) and newspapers (local, outstation). These resources can also be arranged year-wise, subject-wise.
- Time: 30 minutes
Procedure (part 2)
- List animals and plants you have seen in your surrounding and you know according to the habitat. Make columns as below and enter . {| border="1" |- | Animals on land | Animals in water | Amphibians | Plants in forests | Plants in water |}
- Time : 30 minutes
- Video-clippings
- Questions for discussions
Systems of Classification
There are three main system of classification
(i) Artificial
(ii) Natural
(iii)
Phylogenetic
1.
''''Artificial
system of classification'
This
system is based on few morphological characters. First introduced by
Pliny and later on by Aristotle, Theophrastus, Linnaeus, Bauhin, etc.
This system has several lacunae.
2. 'Natural
system of classification'
It is based on a number of characters of organisms that are
classified on the basis of Morphology, Anatomy, Cytology, Physiology,
Ontogeny, Phylogeny, Biochemistry etc. This was given by Schimper,
Eichler, Bentham & Hooker.
3.
''''Phylogenetic
System of Classification'
This Classification is based on evolutionary interrelationships
of organisms. Phylogenetic
system is also called cladistics.
A
Cladogram based on Phenetic is called Dendrogram.
This was proposed
by Engler & Prantl. Hutchinson, Takhtajan, Dobzhansky & Mayr
are modern phylogenetist.
1. Artificial System of Classification --- Contribution of Indians:
(Source: wikipedia)
 The
earliest attempt towards classification of living organisms is seen
in the works of many ancient philosophers in Greek
and India.
The
earliest attempt towards classification of living organisms is seen
in the works of many ancient philosophers in Greek
and India.
1.
Charaka:
The information available from many ancient scriptures of our country
indicates the attempts made by Indians towards classification of
plants and animals. An ancient sage by name Charaka
who
lived in the first century A.D., had listed about 340 plant types and
about 200 animals types in his treatise Charaka
Samhitha.
2. Parashara:
Another
ancient sage by name Parashara
in his treatise Vrikshayurveda
had given a vivid description of plants based on the
characteristics in flowers. He had divided plants into several
“ganas” (families) based on these characters. The description of
characters for these ganas, given by Parashara, is very close to the
ones given by our modern taxonomists.
( Refer – India's Glorius Scientific Traditions Chapter 15 Page no.
148- 155)
 3.
Sushruta: The Sushruta Samhita is one of two early
texts that form the cornerstone of the Indian medical tradition of
Ayurveda (Ayurveda means science of life). The other treatise is
called the Charaka Samhita. Like the Charaka Samhita, the Sushruta
Samhita made revisions and alterations to an earlier text on which it
is based, in this case, the writingsof Divodasa Dhanvantari, the
author's teacher. The author, Sushruta, is identified as the son of
the Vedic sage Visvamitra. The text is long, running over 1,700 pages
in English translation. The exact date of its composition is unknown,
but is generally thought to be around 100A.D.
3.
Sushruta: The Sushruta Samhita is one of two early
texts that form the cornerstone of the Indian medical tradition of
Ayurveda (Ayurveda means science of life). The other treatise is
called the Charaka Samhita. Like the Charaka Samhita, the Sushruta
Samhita made revisions and alterations to an earlier text on which it
is based, in this case, the writingsof Divodasa Dhanvantari, the
author's teacher. The author, Sushruta, is identified as the son of
the Vedic sage Visvamitra. The text is long, running over 1,700 pages
in English translation. The exact date of its composition is unknown,
but is generally thought to be around 100A.D.
Like the Charaka Samhita, the Sushruta Samhita refers to the eight
branches of Ayurvedic medicine. Sushruta is organized similarly to
Charaka, but in addition to emphasizing therapeutics, it also
discusses surgery, which Charaka barely mentions.
Sushruta details about 650 drugs of animal, plant, and mineral
origin. The
conquest by Arabs of the Indian province of Sind (now a part of
Pakistan)in the eighth century unleashed a scholarly exchange of
scientific ideas. The Sushruta samhita was translated into Arabic and
later into Persian.These translations, as well as those of Charaka,
helped to spread the science of Ayurveda far beyond India.
Additional web resources
- Sushruta, Information about Sushruta
- www.faqs.org/health/topics/50/Sushruta.html#ixzz22woKO3cr
- Classification of Living Organisms
Ancient through medieval times
 The
famous Greek philosopher (384 to 322 B.C.) had identified different
types of plants and animals. Apart from this, he described some
organisms under an intermediate group indicating that such organisms
could be placed neither under plants nor under animals. He tried to
classify the organisms on the basis of their form and habitat.
There are many other examples of ancient classification systems that
are based mainly on superficial characteristics. Such systems of
classification are hence described as artificial systems of
classification.
The
famous Greek philosopher (384 to 322 B.C.) had identified different
types of plants and animals. Apart from this, he described some
organisms under an intermediate group indicating that such organisms
could be placed neither under plants nor under animals. He tried to
classify the organisms on the basis of their form and habitat.
There are many other examples of ancient classification systems that
are based mainly on superficial characteristics. Such systems of
classification are hence described as artificial systems of
classification.
Limitations of the artificial system of classification
- The criteria used for classification are superficial and do not reflect the natural relationships.
- The system does not reflect the evolutionary relationship between the organisms.
- Many unrelated organisms are placed in the same group on the basis of their habitats (dwelling place) (For The system does not reflect the evolutionary relationship between the organisms.
- Many unrelated organisms are placed in the same group on the basis of their habitats (dwelling place) (For example, whales and fishes in the same group).
- Closely related organisms have been placed in different groups because of the differences in their habitat, feeding habits, etc.
2. Natural System of Classification
As science became a part of human life, the classification of living organisms had to undergo a thorough modification. The advent of the microscope in the 17th century opened up a new world of organisms that were hitherto unexplored; the world of micro organisms. It was hard to believe the vast diversity that existed in the microscopic world. Scientists started looking for more and more details about different groups of organisms. Various aspects of life such as mode of reproduction, pattern of development, began to be investigated. As a result, more and more similarities and differences started emerging between the different groups in both plants and animals. This led to a more systematic and scientific approach to classification, which is now known as the natural system of classification.
Advantages of natural classification over artificial classification
- It avoids the heterogeneous grouping of unrelated organisms.
- It helps in placing only related groups of organisms together.
- It indicates the natural relationships among organisms.
- It also provides a clear view on the evolutionary relationship between different groups of living organisms.
The initial attempt towards a natural system of classification came from an English biologist, John Ray (1627-1705). He identified a large number of plants and animals based on natural relationships among themselves and classified them into specific groups. He was probably the first biologist to have developed the modern concept of a species. He described the species as an assemblage of individuals derived from similar parents and having the ability to pass on their characteristics to the subsequent generations. He published a three-volume compendium - Historia Generalis Plantarum in which he has given a detailed description of over 18,000 types of plants.
Linnaeus Classification
The natural system of classification was placed on a firm footing by the Swedish biologist, Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778). Linnaeus classified living organisms into two kingdoms the plant kingdom and the animal kingdom. He recorded nearly 6,000 species of plants in his book Species Plantarum published in 1753. He listed more than 4,300 species of animals. He has given detailed system of his classification in another book Systema Naturae. Carolus Linnaeus' great work, the Systema Naturæ (1st ed. 1735), ran through twelve editions during his lifetime. In this work, nature was divided into three kingdoms: mineral, vegetable and animal. Linnaeus used five ranks: class, order, genus, species, and variety.
Linnaeus Taxonomy
 Linnaeus
is best known for his introduction of the method still used to
formulate the scientific name of every species. Before Linnaeus, long
many-worded names (composed of a generic name and a differentia
specifica) had been used, but as these names gave a description of
the species, they were not fixed. In his Philosophia Botanica (1751)
Linnaeus took every effort to improve the composition and reduce the
length of the many-worded names by abolishing unnecessary rhetorics,
introducing
new descriptive terms and defining their meaning with an
unprecedented precision. In the late 1740s Linnaeus began to use a
parallel system of naming species with nomina trivialia. Nomen
triviale, a trivial name, was a single- or two-word epithet placed on
the margin of the page next to the many-worded "scientific"
name. The only rules Linnaeus applied to them was that the trivial
names should be short, unique within a given genus, and that they
should not be changed. Linnaeus consistently applied nomina trivialia
to the species of plants in Species Plantrum (1st edn. 1753) and to
the species of animals in the 10th edition of Systema Naturæ (1758).
Linnaeus
is best known for his introduction of the method still used to
formulate the scientific name of every species. Before Linnaeus, long
many-worded names (composed of a generic name and a differentia
specifica) had been used, but as these names gave a description of
the species, they were not fixed. In his Philosophia Botanica (1751)
Linnaeus took every effort to improve the composition and reduce the
length of the many-worded names by abolishing unnecessary rhetorics,
introducing
new descriptive terms and defining their meaning with an
unprecedented precision. In the late 1740s Linnaeus began to use a
parallel system of naming species with nomina trivialia. Nomen
triviale, a trivial name, was a single- or two-word epithet placed on
the margin of the page next to the many-worded "scientific"
name. The only rules Linnaeus applied to them was that the trivial
names should be short, unique within a given genus, and that they
should not be changed. Linnaeus consistently applied nomina trivialia
to the species of plants in Species Plantrum (1st edn. 1753) and to
the species of animals in the 10th edition of Systema Naturæ (1758).
Binomial Nomenclature
By consistently using these specific epithets, Linnaeus separated nomenclature from description. Even though the parallel use of nomina trivialia and many-worded descriptive names continued until late in the eighteenth century, it was gradually replaced by the practice of using shorter proper names consisting of the generic name and the trivial name of the species. In the nineteenth century, this new practice was codified in the first Rules and Laws of Nomenclature, and the 1st edition of Species Plantarum and the 10th edn. Of Systema Naturae were chosen as starting points for the Botanical and Zoological Nomenclature respectively. This convention for naming species is referred to as binomial nomenclature. Today, nomenclature is regulated by nomenclature codes, which allows names divided into taxonomic ranks.
How is this done?
The present system of binomial nomenclature identifies each species by a scientific name of two words, Latin in form and usually derived from Greek or Latin roots. The first name (capitalized) is the genus of the organism, the second (not capitalized) is its species. The scientific name of the white oak is Quercus alba,while red oak is Quercus rubra. The first name applies to all species of the genus—Quercus is the name of all oaks—but the entire binomial applies only to a single species. Many scientific names describe some characteristic of the organism (alba=white; rubra=red); many are derived from the name of the discoverer or the geographic location of the organism. Genus and species names are always italicized when printed; the names of other taxa (families, etc.) are not. When a species (or several species of the same genus) is mentioned repeatedly, the genus may be abbreviated after its first mention, as in Q. alba. Subspecies are indicated by a trinomial; for example, the southern bald eagle is Haliaeetus leucocephalus leucocephalus, as distinguished from the northern bald eagle, H. leucocephalus washingtoniensis.
The
advantages of scientific over common names are that they are accepted
by speakers of all languages, that each name applies only to one
species, and that each species has only one name. This avoids the
confusion that often arises from the use of a common name to
designate different things in different places (for example, see
elk),
or from the existence of several common names for a single species.
There are two international organizations for the determination of
the rules of nomenclature and the recording of specific names, one
for zoology and one for botany. According to the rules they have
established, the first name to be published (from the work of
Linnaeus on) is the correct name of any organism unless it is
reclassified in such a way as to affect that name (for example, if it
is moved from one genus to another). In such a case definite rules of
priority also apply.
FEW
EXAMPLES ARE GIVEN BELOW:
|
Animals
|
Plants
|
|
Man
-Homo
Sapiens
|
Peepal
-Ficus
religiosa
|
3. Phylogenetic Classification: Modern system
File:Background Material - Organisms html m3f176432.jpg
While the earlier systems of classification focused on habitats and characteristics, the current system of classification is based on evolutionary history, to improve consistency with the Darwinian principle of common descent. With the introduction of the cladistic method in the late 20th century, phylogenetic taxonomy in which organisms are grouped based purely on inferred evolutionary relatedness, ignoring morphological similarity, has become common in some areas of biology.[1] Molecular phylogenetics, which uses DNA sequences as data, has also driven many recent revisions and is likely to continue doing so.
Where
as Linnaeus classified for ease of identification, the idea of the
Linnaean taxonomy as
translating into a sort of dendrogram of
the Animal-
and Plant Kingdoms was
formulated toward the end of the 18th century, well before the Origin
of Species was
published. Among early works exploring the idea of transmutation
of species was
Erasmus Darwin's
1796 Zoönomia and
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck's
Philosophie Zoologique of 1809.
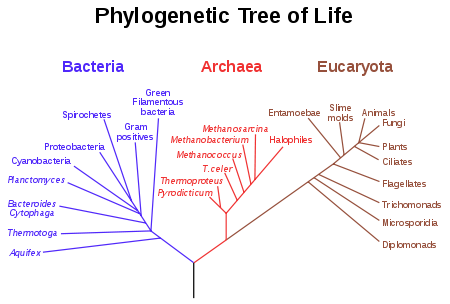 With
Darwin's theory, a general acceptance that classification should
reflect the Darwinian principle of common
descent quickly
appeared. Tree of Life representations
became popular in scientific works, with known fossil groups
incorporated. One of the first modern groups tied to fossil ancestors
were birds.
Using the then newly discovered fossils of Archaeopteryx and
Hesperornis,
Thomas Henry Huxley pronounced
that they had evolved from dinosaurs, a group formally named by
Richard Owen in
1842. The
resulting description, that of dinosaurs "giving rise to"
or being "the ancestors of" birds, is the essential
hallmark of evolutionary
taxonomic
thinking.
As more and more fossil groups were found and recognized in the
late 19th and early 20th century, palaeontologists worked
to understand the history of animals through the ages by linking
together known groups.
With
the modern evolutionary
synthesis of
the early 1940s, an essentially modern understanding of evolution of
the major groups was in place. The evolutionary taxonomy being based
on Linnaean taxonomic ranks, the two terms are largely
interchangeable in modern use.
With
Darwin's theory, a general acceptance that classification should
reflect the Darwinian principle of common
descent quickly
appeared. Tree of Life representations
became popular in scientific works, with known fossil groups
incorporated. One of the first modern groups tied to fossil ancestors
were birds.
Using the then newly discovered fossils of Archaeopteryx and
Hesperornis,
Thomas Henry Huxley pronounced
that they had evolved from dinosaurs, a group formally named by
Richard Owen in
1842. The
resulting description, that of dinosaurs "giving rise to"
or being "the ancestors of" birds, is the essential
hallmark of evolutionary
taxonomic
thinking.
As more and more fossil groups were found and recognized in the
late 19th and early 20th century, palaeontologists worked
to understand the history of animals through the ages by linking
together known groups.
With
the modern evolutionary
synthesis of
the early 1940s, an essentially modern understanding of evolution of
the major groups was in place. The evolutionary taxonomy being based
on Linnaean taxonomic ranks, the two terms are largely
interchangeable in modern use.
Phylogenetic Nomenclature
Since the 1960s a trend called phylogenetic nomenclature (or cladism) has emerged, inspired by the cladistic method. The salient feature is arranging taxa in a hierarchical evolutionary tree, ignoring ranks. If a taxon includes all the descendants of some ancestral form, it is called monophyletic. Groups that have descendant groups removed from them (e.g. dinosaurs, with birds as offspring group) are termed paraphyletic, while groups representing more than one branch from the tree of life are called polyphyletic. A formal code of nomenclature, the International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature, or PhyloCode for short, is currently under development, intended to deal with names of clades. Linnaean ranks will be optional under the PhyloCode, which is intended to coexist with the current, rank-based codes.
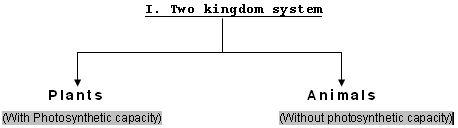
Kingdoms and domains
Two
Kingdom System
When
Linnaeus developed his classification, there were only plants and
animals kingdoms. With the microscope came the discovery of many
more kingdoms of living organisms.
From
well before Linnaeus, plants and animals were considered separate
Kingdoms.
Linnaeus used this as the top rank,
dividing the physical world into the plant, animal and mineral
kingdoms. As advances in microscopy made classification of
microorganisms possible, the number of kingdoms increased, five
and six-kingdom systems being the most common.
Domains
are a relatively new grouping. The three-domain system
was first proposed in 1990, but not generally accepted until
later. One main characteristic of the three-domain method is the
separation of Archaea
and Bacteria,
previously grouped into the single kingdom Bacteria (a kingdom
also sometimes called Monera).
Consequently, the three domains of life are conceptualized as
Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryota
(comprising the nuclei-bearing
eukaryotes).
A small minority of scientists add Archaea as a sixth kingdom, but
do not accept the domain method.
Thomas
Cavalier-Smith,
who has published extensively on the classification of protists,
has recently proposed that the Neomura,
the clade that groups together the Archaea
and Eukarya,
would have evolved from Bacteria,
more precisely from Actinobacteria.
His classification of 2004 treats the archaebacteria as part of a
subkingdom of the Kingdom Bacteria, i.e. he rejects the
three-domain system entirely.
Limitations
of two kingdom system
1
Euglena and other similar unicellular organisms have characters of
both animals and plants.
2 Blue green algae (now called
Cyanobactria)
and bacteria having some cytological differences from other
organisms also present as difficulty.
3. Fungi,
which are usually included in plants, have some characters not
common to plants.
4. Instead of two modes of feeding (ingestion
in animals and primarily photosynthesis in plants), now 3 modes
are recognized photosynthetic, ingestion & absorption.
Five Kingdom System
This
was developed by Whittaker in 1969.
1.
Kingdom monera:
(a)Prokaryotic
cells lack Nuclear membrane, Plastids, Mitochondria and advanced
(9+2) strand
flagella.
(b) Reproduction is asexual by fission or budding.
Example
- Blue green algae, Bacteria etc.
2.'''Kingdom
Protista''''':
(a)
They are unicellular or colonial eukaryotic cells.
(b)
Reproduction is asexual and sexual.
Example
unicellular Algae, Diatoms etc.
3.'''Kingdom
plantae''':
(a)
Multicellular organisms with cellulose wall and frequently
vacuolated, eukaryotic cells.
(b) Nutritive mode is
photosynthetic but absorptive.
(c) Reproduction is sexual.
Example
- Rhodophyta, Phaeophyta, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms)
4.'''Kingdom
Fungi''':
(a)
Multinucleate organisms with eukaryotic nuclei.
(b) Plastids
and photosynthetic pigments lacking.
(c) Reproduction asexual
and sexual both. Example - Fungi
5.'''Kingdom
Animalia''':
(
a) Multicellular organisms, eukaryotic cell devoid of cell
wall.
(b) Lack plastids and photosynthetic pigments.
(c)
Organization and tissue differentiation complex
(d)
Reproduction is sexual.
Time line of Classification
|
Linnaeus
|
Haeckel
|
Chatton
|
Copeland
|
Whittaker
|
Woese et al.[[]]]
|
Woese et al.
|
Cavalier-Smith
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2 kingdoms
|
3 kingdoms
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 kingdoms
|
|
(not treated)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Evaluation
1. Which do you think is a more basic
characteristic for classifying organisms?
(a) the place where they live.
(b) the kind of cells they of. Why?
2.What is the primary characteristic on
which the first division of organisms is made?
3. Why is Binomial nomenclature famous.?
Though cat and tiger belong to same family,why are the species
different? Write their systematic position.
Thought provoking question:
1.Why does Polar bear look diffrent from bear in Karnataka? 2. On what bases are plants and animals put into different categories?
Enrichment activity:
1. Many magazines and newspapers talk about possibility of life outside the
Earth.
Read these articles and have a discussion in the class about what
could
be defined as life outside Earth.
- Collect variety of plant leaves, dry and prepare an herbarium. (Diversity -Project work)
- Collect pictures of Charaka , Aristotle and C. Lineus and know their life history.
Self evaluation of teachers:
Teacher evaluates her transaction in teaching-learning process. She frames the following questions for self evaluation and answers it by reflection on her teaching .
- Did I plan for the activities before hand?
- Was I sucessful in implementing these activities?
- Was the participation of students satisfactory?
- Did all students actively participate and answer the questions?
- Was I able to give extra information to students?
- Did students enjoy using various media for learning?
- How can I improve my teaching?
Additional Resources
Suggessted Reading:- 1) PUC Text book .(2)NCERT Text books.
(1)
''Diversity of Living Things www.edu.gov.nf.ca/division/stsuppsv/Junhigh/grad9sci.pdf[[]]
(2)[[]]Classification of Organisms
www.sci.uidaho.edu/.../T2L4P1_Classification_of_Organisms.pdf
(3)
India'S Glorious Scientific Tradition - Google Books Result
books.google.co.in/books?isbn=818430028X...
By Suresh Soni-2009
Websites
1. [[5]]
2. [[6]].
3.
[[7]]
4.
www.youtube.com/watch?v=IW23Qhg2v-0
(To watch video of diversity of organisms.)
5. [[8]]
( for 'diversity
of organisms.)
External links- 1) [[9]].
'C'harakaSamhita - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/''Charaka''_Samhita
Resource Material on Organisms 27/27