Difference between revisions of "User:Ranjani"
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
{| id="mp-topbanner" style="width:100%;font-size:100%;border-collapse:separate;border-spacing:20px;" | {| id="mp-topbanner" style="width:100%;font-size:100%;border-collapse:separate;border-spacing:20px;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style="width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_History The Story of Mathematics] | [http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_History The Story of Mathematics] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "|[http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Philosophy Philosophy of Mathematics] | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " |[http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Philosophy Philosophy of Mathematics] |
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Pedagogy Teaching of Mathematics] | [http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Pedagogy Teaching of Mathematics] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Maths:_Curriculum_and_Syllabus Curriculum and Syllabus] | [http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Maths:_Curriculum_and_Syllabus Curriculum and Syllabus] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Topics Topics in School Mathematics] | [http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Topics Topics in School Mathematics] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Text_Books#Mathematics_-_Textbooks Textbooks] | [http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Text_Books#Mathematics_-_Textbooks Textbooks] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Maths:_Question_Papers Question Bank] | [http://www.karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Maths:_Question_Papers Question Bank] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
# Constants, Variables and Exponenets | # Constants, Variables and Exponenets | ||
===Notes for teachers=== | ===Notes for teachers=== | ||
| − | ''why cant the exponent be a negetive integer? | + | ''why cant the exponent be a negetive integer? '' |
| − | ''because An expression cannot be divided by a variable | + | ''because An expression cannot be divided by a variable'' |
===Activities=== | ===Activities=== | ||
| − | #Activity No #1 [[Defining a polynomial_Activity1|.Introduction to Polynomials]] | + | #Activity No #1 [[Defining a polynomial_Activity1|.Introduction to Polynomials]] |
#Activity No #2 '''Concept Name - Activity No.''' | #Activity No #2 '''Concept Name - Activity No.''' | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
===Activities=== | ===Activities=== | ||
| − | #Activity No #1 | + | #Activity No #1 Types of polynomals 1 |
| − | #Activity No #2 | + | #Activity No #2 Types of polynomals2 |
==Concept 3 Operation on polynomial == | ==Concept 3 Operation on polynomial == | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
##division of a polynomial by polynomial using long division method | ##division of a polynomial by polynomial using long division method | ||
===Notes for teachers=== | ===Notes for teachers=== | ||
| − | ''why cant the exponent be a negetive integer? | + | ''why cant the exponent be a negetive integer? '' |
| − | ''because An expression cannot be divided by a variable | + | ''because An expression cannot be divided by a variable'' |
===Activities=== | ===Activities=== | ||
| − | #Activity No #1 [[Dvision of polynomial_Zero of a polynomial|.verifying Zeroes of aQuadratic polynomial using Geogebra Applet ]] | + | #Activity No #1 [[Dvision of polynomial_Zero of a polynomial|.verifying Zeroes of aQuadratic polynomial using Geogebra Applet]] |
#Activity No #2 '''Concept Name - Activity No.''' | #Activity No #2 '''Concept Name - Activity No.''' | ||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
<div style="width:150px;border:none; border-radius:10px;box-shadow: 5px 5px 5px #888888; background:#ffffff; vertical-align:top; text-align:center; padding:5px;"> | <div style="width:150px;border:none; border-radius:10px;box-shadow: 5px 5px 5px #888888; background:#ffffff; vertical-align:top; text-align:center; padding:5px;"> | ||
| − | ;;[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/index.php/೧೦ನೇ_ತರಗತಿಯ_ಸಮರೂಪ_ತ್ರಿಭುಜಗಳು ಕನ್ನಡದಲ್ಲಿ ನೋಡಿ] | + | ;;[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/index.php/೧೦ನೇ_ತರಗತಿಯ_ಸಮರೂಪ_ತ್ರಿಭುಜಗಳು ಕನ್ನಡದಲ್ಲಿ ನೋಡಿ] |
| + | </div> | ||
<!-- This portal was created using subst:box portal skeleton --> | <!-- This portal was created using subst:box portal skeleton --> | ||
| Line 129: | Line 130: | ||
{| id="mp-topbanner" style="width:100%;font-size:100%;border-collapse:separate;border-spacing:20px;" | {| id="mp-topbanner" style="width:100%;font-size:100%;border-collapse:separate;border-spacing:20px;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style="width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_History The Story of Mathematics] | [http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_History The Story of Mathematics] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "|[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Philosophy Philosophy of Mathematics] | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " |[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Philosophy Philosophy of Mathematics] |
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Pedagogy Teaching of Mathematics] | [http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Pedagogy Teaching of Mathematics] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Maths:_Curriculum_and_Syllabus Curriculum and Syllabus] | [http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Maths:_Curriculum_and_Syllabus Curriculum and Syllabus] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Topics Topics in School Mathematics] | [http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Mathematics:_Topics Topics in School Mathematics] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Text_Books#Mathematics_-_Textbooks Textbooks] | [http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Text_Books#Mathematics_-_Textbooks Textbooks] | ||
| − | |style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; "| | + | | style=" width:10%; border:none; border-radius:5px;box-shadow: 10px 10px 10px #888888; background:#f9f9ff; vertical-align:middle; text-align:center; " | |
[http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Maths:_Question_Papers Question Bank] | [http://karnatakaeducation.org.in/KOER/en/index.php/Maths:_Question_Papers Question Bank] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 147: | Line 148: | ||
= Concept Map = | = Concept Map = | ||
__FORCETOC__ | __FORCETOC__ | ||
| + | |||
[[File:Triangles_.mm |flash]] | [[File:Triangles_.mm |flash]] | ||
| Line 245: | Line 247: | ||
* Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child): | * Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child): | ||
# Think and try : Is it possible to draw a triangle with the condition (AB + BC) < AC | # Think and try : Is it possible to draw a triangle with the condition (AB + BC) < AC | ||
| − | * '''For Geogebra file''' [[http://tube.geogebra.org/m/1482289/ click here | + | * '''For Geogebra file''' [[http://tube.geogebra.org/m/1482289/ click here] ] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 09:44, 12 November 2019
| Philosophy of Mathematics |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist.
Concept Map
Textbook
Please click here for Karnataka and other text books.
Additional Information
Useful websites
- Useful number pattern activities| Useful number pattern activities
- To get the videos on polynomials in Kannadaclick here this is shared by Yakub koyyur, GHS Nada.
Reference Books
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1 Basics of polynomial
Learning objectives
- Defining of a Polynomial
- What is an expression?
- Constants, Variables and Exponenets
Notes for teachers
why cant the exponent be a negetive integer? because An expression cannot be divided by a variable
Activities
- Activity No #1 .Introduction to Polynomials
- Activity No #2 Concept Name - Activity No.
Concept 2 Types of Polynomials
Learning objectives
- defining monomial, binomial, trinomial and polynomial
Notes for teachers
These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.
Activities
- Activity No #1 Types of polynomals 1
- Activity No #2 Types of polynomals2
Concept 3 Operation on polynomial
Learning objectives
- Additon of polynomial
- Substraction of a Polynomial
- Multiplication of a polynomial
- Product of Monomial and a Binomial
- Product of two binomial
- finding product of binomial as Idenitity
- Expansion of Polynomial using Identities
- Divison of a polynomial
- division algoritham for polynomial
- Zeroes of a Polynomial
- division of a polynomial by linear polynomial
- Remainder theorem
- Factor theorem
- Syntheic divsion
- division of a polynomial by polynomial using long division method
Notes for teachers
why cant the exponent be a negetive integer? because An expression cannot be divided by a variable
Activities
- Activity No #1 .verifying Zeroes of aQuadratic polynomial using Geogebra Applet
- Activity No #2 Concept Name - Activity No.
Concept 4 Degree of a polynomial
- this video helps to know the degree of polynomial
Learning objectives
- Degree of polynomial with one variable
- constant polynomial
- Linear polynomial
- Quadratic polynomial
- Cubic Polynomial
- Quatric polynomial
Notes for teachers
These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.
Activities
- Activity No #1 Concept Name - Activity No.
- Activity No #2 Concept Name - Activity No.
Notes for teachers
These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.
Activities
- Activity No #1 Concept Name - Activity No.
- Activity No #2 Concept Name - Activity No.
Assessment activities for CCE
Evaluates the zero of a polynomial by graphical representation
Hints for difficult problems
'''Solution for the Problems of Chapter 8-Polynomials 10 STD'''
Project Ideas
Math Fun
| Philosophy of Mathematics |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist.
Concept Map
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional Information
http://www.mathopenref.com/similartriangles.html
Useful websites
- All about triangles :This is a reference website for types and classification off triangles
- http://www.regentsprep.org/regents/math/geometry/GPB/theorems.htm :A good website for quick reference of all theorems in geometry. Suitable for both students and teachers.
- Click here for notes on types of triangles.
- to get the videos on similar triangle in Kannada click herethis is shared by Yakub koyyur GHS Nada.
Reference Books
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1 A triangle and its basic properties
Learning objectives
- A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments.
- It is the polygon with the least number of sides.
- A triangle can be defined as a polygon which has 3 sides, 3 angles and 3 vertices.
- The sum of any two sides is always greater than the third side.
- The angle opposite to longest side is the largest.
- The angles inside the triangle are its interior angles.
- The sum of all 3 interior angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees which is called the angle sum property of a triangle.
- The external angle of a triangle is always equal to the sum of its two opposite interior angles.
Notes for teachers
[These are short notes that the teacher wants to share about the concept, any locally relevant information, specific instructions on what kind of methodology used and common misconceptions/mistakes.]
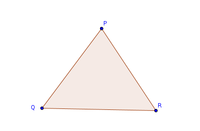
- A triangle PQR consists of all the points on the line segment PQ,QR and RP. The three line segments, PQ, QR and RP that form the triangle PQ, are called the sides of the triangle PQR.
- A triangle has three angles. In figure, the three angles are ∠PQR ∠QRP and ∠RPQ
- A triangle has six parts, namely, three sides,PQ QRand RP.Three angles ∠PQR ∠QRP and ∠RPQ. These are also known as the elements of a triangle.
- The point of intersection of the sides of a triangle is known as its vertex. In figure, the three vertices are P, Q and R. In a triangle, an angle is formed at the vertex. Since it has three vertices, so three angles are formed. The word triangle =tri + angle ‘tri’ means three. So, triangle means closed figure of straight lines having three angles.
Activity No # 1 Make your triangle
- Estimated Time - 40 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed; Paper, pencil, and scale.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any:
- The students should know points and line segments.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ Geogebra Applets
- Process (How to do the activity):
- Mark three non-collinear point P, Q and R on a paper.
- Join these points in all possible ways. The segments are PQ, QR and RP.
- A simple close curve formed by these three segments is called a triangle. It is named in one of the following ways.
- Triangle PQR or Triangle PRQ or Triangle QRP or Triangle RPQ or Triangle RQP .
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions):
- What are plane figures ?
- What is a polygon ?
- How many points are needed to make a traingle ?
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child):
- What are the intersecting points of a triangle called ?
- Can you draw a triangle with collinear points.
- Question Corner
- Name the elements of a triangle.
Activity No # 2. Angle sum property of a triangle
Please click the following link for the proof
- Estimated Time: 40 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed:Laptop, projector, geogebra file and a pointer.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any:
- Basics of triangles should have been covered.
- Angles formed when a traversal cuts a pair of parallel lines and the relationship between them should have been taught.
Activity No # 3. Side sum property of a triangle
- Estimated Time - 20 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed; Paper, pencil, and scale.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any:
- The students should know to construct triangle.
- Process (How to do the activity):
- Mark three non-collinear point A, B and C on a paper.
- Join these points in all possible ways. The segments are AB, BC & AC
- Measure the sides AB, BC & AC
- Find the relationship between AB + BC with AC
- Find the relationship between AC + BC with AB
- Find the relationship between AB + AC with BC
- Developmental Questions (What discussion questions):
- What relationship do you observe ?
- Evaluation (Questions for assessment of the child):
- Think and try : Is it possible to draw a triangle with the condition (AB + BC) < AC
- For Geogebra file [click here ]