Difference between revisions of "Activity1 Pi the mathematical constant"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "===Name of the activity=== Brief blurb describing what the activity. If this has been borrowed from some external web site (for example, a non OER or OER site which had this...") |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Objectives === | === Objectives === | ||
| − | + | Students will be able to understand the value of Pi is ratio of circle's circumference to its diameter. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Estimated Time=== | ===Estimated Time=== | ||
| + | 40minutes | ||
=== Prerequisites/Instructions, prior preparations, if any === | === Prerequisites/Instructions, prior preparations, if any === | ||
| + | Know the concepts of circumference and diameter of a circle. | ||
===Materials/ Resources needed=== | ===Materials/ Resources needed=== | ||
| − | + | Digital resources:[[:File:Pi the Mathematical Constant.ggb|Click here to open the file]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Non digital resources: | |
| + | * finding the perimeter of a circle using thread and diving it by using diameter. | ||
| − | + | ===Process (How to do the activity)=== | |
| + | ##[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_rJdkhlWZVQ&feature=youtu.be Click here for Finding Pi by Archimedes Method]. Archimedes approximated the value of Pi by starting with the fact that a regular hexagon inscribed in a unit circle has a perimeter of 6. He then found a method for finding the perimeter of a polygon with twice as many sides. Applying his method repeatedly, he found the perimeter of a 12, 24, 48, and 96 sided polygon. Using the perimeter as an approximation for the circumference of a circle he was able to derive an approximation for Pi equivalent to 3.14. This video uses a somewhat simpler method of doing the same thing and carries it out to polygons with millions of sides. All that is needed to understand the calculation is knowledge of the Pythagorean Theorem. | ||
| + | ##{{Geogebra|zvbqkqa7}} | ||
| + | #[http://geogebratube.org/material/show/id/144079 Geogebra file] for explaining how 'circumference / diameter' is a constant, denoted as pi (Greek letter), using a number line | ||
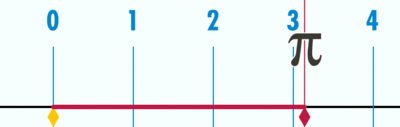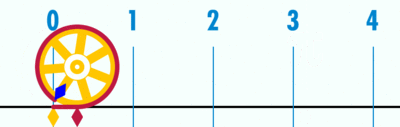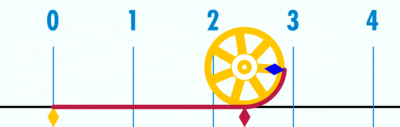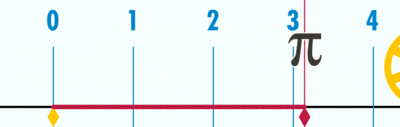
| + | #An animation of the same concept. | ||
| + | [[File:Pi 121.gif|400px|link=]] | ||
| + | *Process/ Developmental Questions | ||
| + | Open the Geogebra file. Move the slider to 'unravel' the circumference' over the number line. Since the diameter is 1 unit (measuring from -0.5 to 0.5 on number line), the circumference ends at 3.14, showing the ratio between circumference | ||
| + | *Evaluation | ||
| − | + | *Question Corner | |
| + | if the diameter is increased from 1 to 2, what will the circumference be? | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Circles]] | |
Latest revision as of 08:29, 15 July 2020
Objectives
Students will be able to understand the value of Pi is ratio of circle's circumference to its diameter.
Estimated Time
40minutes
Prerequisites/Instructions, prior preparations, if any
Know the concepts of circumference and diameter of a circle.
Materials/ Resources needed
Digital resources:Click here to open the file
Non digital resources:
- finding the perimeter of a circle using thread and diving it by using diameter.
Process (How to do the activity)
- Click here for Finding Pi by Archimedes Method. Archimedes approximated the value of Pi by starting with the fact that a regular hexagon inscribed in a unit circle has a perimeter of 6. He then found a method for finding the perimeter of a polygon with twice as many sides. Applying his method repeatedly, he found the perimeter of a 12, 24, 48, and 96 sided polygon. Using the perimeter as an approximation for the circumference of a circle he was able to derive an approximation for Pi equivalent to 3.14. This video uses a somewhat simpler method of doing the same thing and carries it out to polygons with millions of sides. All that is needed to understand the calculation is knowledge of the Pythagorean Theorem.
Download this geogebra file from this link.
- Geogebra file for explaining how 'circumference / diameter' is a constant, denoted as pi (Greek letter), using a number line
- An animation of the same concept.
- Process/ Developmental Questions
Open the Geogebra file. Move the slider to 'unravel' the circumference' over the number line. Since the diameter is 1 unit (measuring from -0.5 to 0.5 on number line), the circumference ends at 3.14, showing the ratio between circumference
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
if the diameter is increased from 1 to 2, what will the circumference be?