Mensuration
| Philosophy of Mathematics |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist.
Concept Map
Error: Mind Map file Mensuration.mm not found
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional Information
Useful websites
1. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/allgcse/bs7act1.pdf
This is a good website for interesting activities on mensuration.
2.For standard measurements : http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/maths/mathsE1.htm
3.For general rules while writing units ://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_System_of_Units#General_rules
4.For teacher reference on dimension. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/163641/dimension
Reference Books
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1. What is Mensuration ?
Learning objectives
- The students learn that mensuration is the branch of Mathematics dealing with measurement of angles, length, area, and volume.
- Students will learn and understand that it is important to know how to measure things.
- They should have a clear distinction of different measuring/calculating parameters
- They should understand the characteristics of different figures.
- The length of the total boundary of a figure is called its perimeter. The Metric unit of perimeter is same as the unit of length - Metre.
- The perimeter of 2D geometrical figures like quadrilaterals can be obtained by calculating the sum of all the sides of the figure.
- The amount of surface covered by an object is called it area. The Metric unit of area is square metre.
- The capacity of an object to hold is called its volume.
- Develop an appreciation towards derivation of formula for calculations.
- They should develop the ability to calculate the area, perimeter, volume or side of many different figures.
Notes for teachers
Measurement are an important part of our everyday life. Think about your day; you probably made some measurements.Perhaps you checked your weight by stepping on a scale,measuring shoes to fit your feet in the shoe store, or saw measuring up houses when they are doing renovations etc. If you did not feel well, you may have taken your temperature. To make some soup, you added 2 cups of water to a package mix. If you stopped at the Petrol bunk, you watched the petrol pump measure the number of litres of petrol you put in the car. Measurement is an essential part of every aspect of life. The temperature, height, and weight of a patient are measured and recorded.Samples of blood and urine are collected and sent to a laboratory where glucose, pH, urea, and protein are measured by the lab technicians.By learning about measurement, you will develop skills for solving problems.
Activity No # Importance of measurements and calculations - a discussion
- Estimated Time :45 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed : Note book, pen
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process:
- Ask the children to make a list of all activities in different areas of life where measurements play an important role.
- Have a discussion in the classroom regarding importance of measurements and how difficult life would be without measurements.
Developmental Questions:
- Why measure ?
- How do we measure ?
- Evaluation:
- What are the measuring modes and units seen at the market, Hospital, Chemist laboratories, Gold shop, Tailors, Bakeries, Petrol bunks, water tankers, milk vendors, contractors, kitchen, airport, and so on.?
- Question Corner:
- What were the early crude measuring modes used. Find out from your elders.
- Why do you think certain measuring standards are needed ?
- Who formulates the standards
Activity No # Tangram
This activity has been taken from the website :http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/allgcse/bs7act1.pdf
- Estimated Time : 40 minutes.
- Materials/ Resources needed: Chart papers, scissors, pencil, scale.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- The students should have understanding of basic shapes like square, rectangle, parallelogram, triangle and trapezium.
- They should be able to draw mentioned shapes accurately and cut exactly on boundaries.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process:
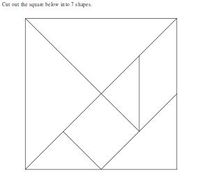
- This is a very old Chinese puzzle known as a tangram.
- Cut out the square below into 7 shapes.
- Cut out the 7 shapes and rearrange them to form:
(a) a square from two triangles, and then change it to a parallelogram; (b) a rectangle using three pieces, and then change it into a parallelogram; (c) a trapezium with three pieces; (d) a parallelogram with four pieces; (e) a trapezium from the square, parallelogram and the two small triangles; (f) a triangle with three pieces; (g) a rectangle with all seven pieces.
- Finally, put the pieces back together to form the original square.
- Developmental Questions:
- Were you all able to read and follow the instructions.
- Name and point the different shapes in the figure.
- Name the dimensions of each shape.
- Evaluation:
- Analyse how much space each shape is occupying.
- What can you refer to the space occupied by each shape.
- Question Corner:
- What are the characteristic properties of each shape: square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram and trapezium ?
- What type of two triangles would you need to form a square ?
- What did you learn from this activity ?
Concept #2.Informal units of measurements
Learning objectives
- The students understand that informal ways of measurements are a type of measure which uses non-standard units such as hand spans, armlengths, footsteps or pattern blocks to measure length, area, etc.
- They comprehend that estimate and informal measurement are interchangeable terms.
- They realise that informal measurements are not always the same but vary with the person involved in measuring.
Notes for teachers
- The teacher can ask the students to gather information regarding earlier informal measuring ways from their elders and have an initial discussion in the classroom.
Activity No # 1. Estimating distances
- Estimated Time :1 hour
- Materials/ Resources needed : Sticks, ropes, writing pad, pencil.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- The students should have been introduced to different forms of informal measurements.
- They should have the ability to measure and document their findings accurately.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process:
- The teacher can ask the students to determine the distances of library, principal's room, playground, dining hall, entrance gate from their classroom using various informal measuring methods.
- The children can decide which method to use - whether foot, sticks or ropes.
- The task can be done in groups of 3 children.
- Document and compare the results.
- Discuss regarding the length of distance.
- Developmental Questions:
- Which point would we mark as the point of reference for measuring our classroom.
- Similarly what are the points of reference for other places.
- How do we mark them.
- Which measuring unit have you chosen ?
- How will you document the findings ?
- How can we tabulate our findings on board for comparisons ?
- What would be our report back time ?
- What are our findings ?
- What conclusions can we draw ?
- Evaluation:
- What have we learnt so far about measuring object?
- Question Corner:
- How can we measure curves?
- What are the problems with informal measuring units?
- Can we think of methods to measure so that measures taken by anyone would always be same for a given object or distance.
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #3. Standard units of measurements
Learning objectives
- They should understand that there is no natural unit for the measurement of surfaces. It is necessary to fix upon an artificial unit and that , that artificial unit is a square. To find the area of a surface is to find how many times this measuring unit can be applied to or is contained times in the given figure.
- It is essential for students to have an understanding of the units used to measure .
Notes for teachers
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #4. Scale drawing
Learning objectives
Notes for teachers
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Hints for difficult problems
Project Ideas
Math Fun
Usage
Create a new page and type {{subst:Math-Content}} to use this template